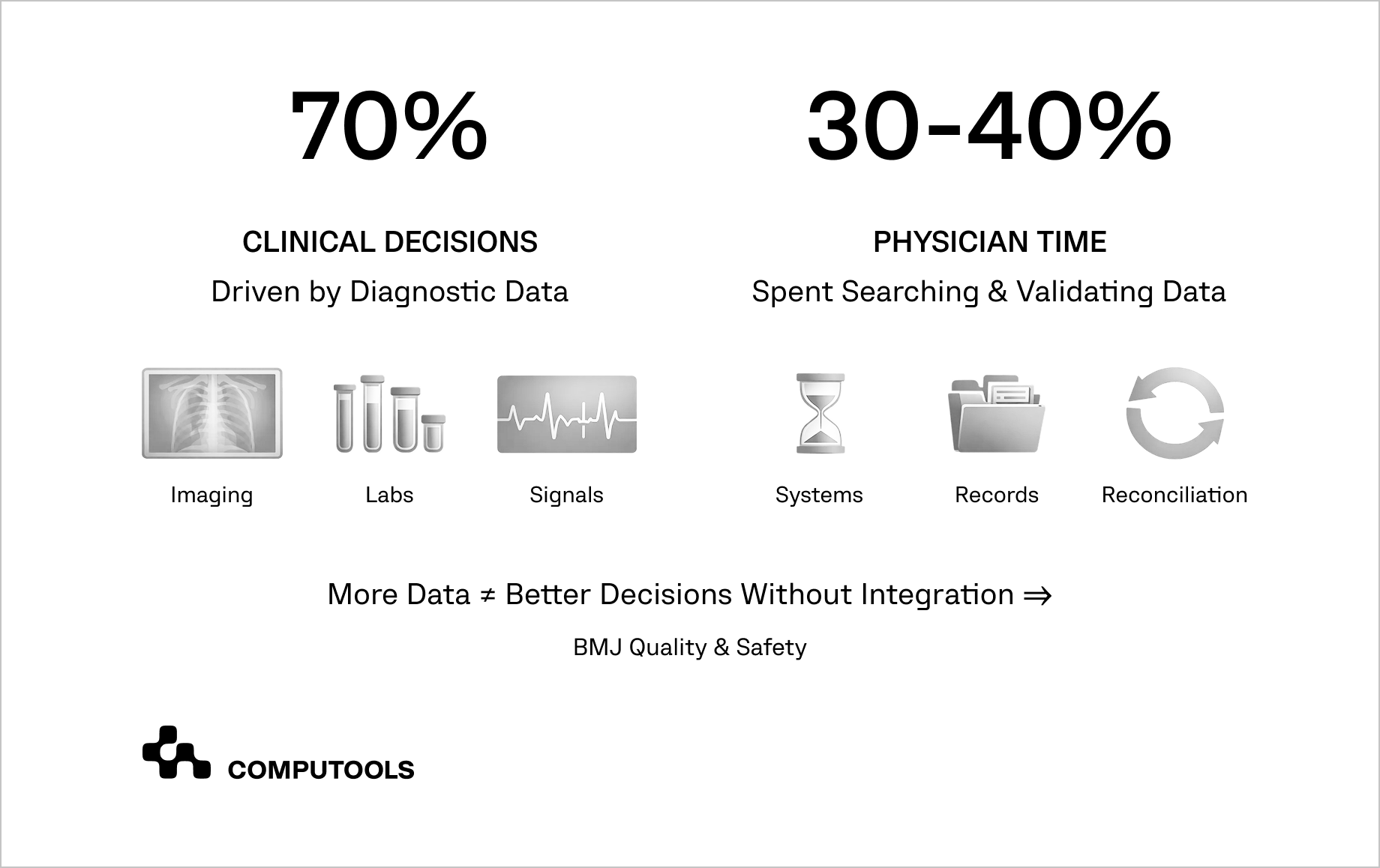
To integrate AI into hospital systems effectively, healthcare organizations first need to confront a structural reality: modern hospitals operate in an environment where diagnostic data drive most clinical decisions, yet that data remains scattered, time-consuming to verify, and prone to interpretation errors.
According to research published in BMJ Quality & Safety, up to 70% of clinical decisions rely directly on diagnostic inputs, including medical imaging, laboratory results, and physiological signals. At the same time, physicians spend approximately 30–40% of their working hours searching for, reconciling, and validating patient information across fragmented systems.
This workload extends well beyond scheduled shifts: clinicians average 45 hours per week in clinical duties and an additional 15 hours on administrative tasks such as documentation and follow-ups, which increasingly reduces time available for direct patient care and contributes to unsustainable pressure and burnout.
This fragmentation comes at a measurable cost. Diagnostic errors are a leading cause of delayed treatment, unnecessary procedures, and avoidable costs. Most people experience at least one diagnostic error, which is linked to serious clinical and financial consequences. AI diagnostics offer a promising solution — faster analysis, large-scale pattern recognition, and decision support beyond human capabilities.
With U.S. healthcare spending reaching $4.9 trillion in 2023, health systems face growing pressure to improve efficiency within highly constrained operational environments. Digital and AI investments offer a clear path forward, but value emerges only when these capabilities are integrated into existing hospital systems rather than deployed as standalone tools.
According to McKinsey & Company, organizations that focus on high-impact digital and analytics initiatives while modernizing legacy infrastructure can unlock $200 billion to $360 billion in value across the healthcare ecosystem. This turns AI diagnostics for hospitals from isolated experimentation into a scalable driver of clinical and operational performance.
How we integrated AI diagnostics into real-world hospital workflows
The challenge we faced with MediDirect wasn’t a lack of advanced technology but the real-world operation of modern healthcare settings. As a healthcare startup, MediDirect aimed to create a platform that truly enhanced efficiency across medical facilities, supporting physicians, nurses, and administrators within a unified digital ecosystem.
From the start, the goal was to integrate intelligence into everyday clinical workflows, not to implement AI as a standalone innovation.
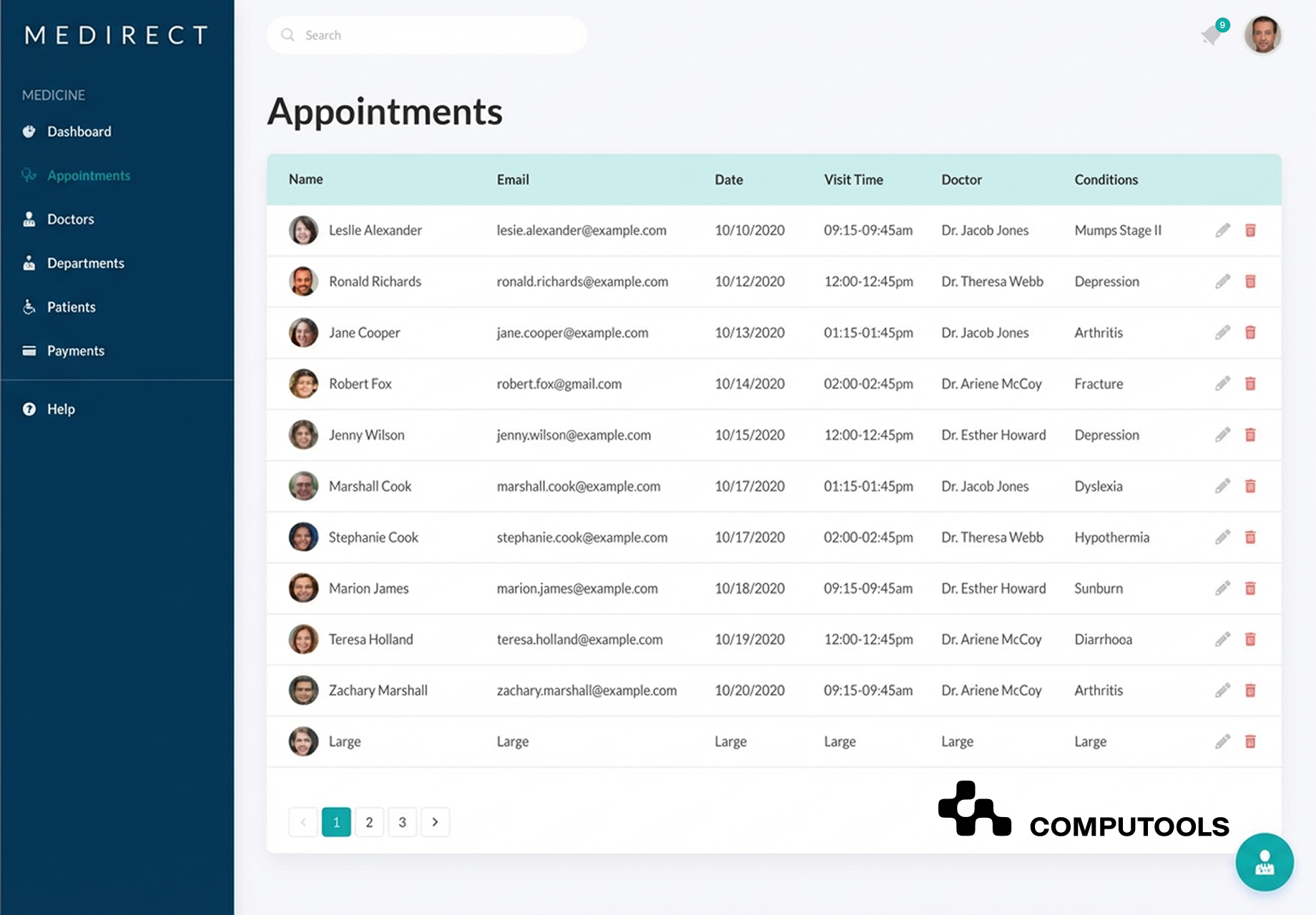
At the core of the problem was fragmentation. Patient data, medical histories, prescriptions, and scheduling information originated from multiple sources, each with its own calculation logic and data structure. This made consistent analysis difficult, slowed clinical decision-making, and increased the risk of errors. Applying AI diagnostics on top of such an environment without first addressing data consistency would have amplified operational complexity rather than reduced it.
Our work began with architecture. We designed a centralized platform that unified disparate data sources and introduced standardized calculation and processing logic across the system. This foundation enabled reliable analytics and created the conditions required for AI development services to deliver real clinical value rather than isolated insights.
Once data flows were normalized and traceable, AI capabilities were embedded directly into existing interfaces. Instead of introducing new dashboards, diagnostic insights were generated automatically in the background and surfaced within familiar screens. This approach allowed AI in hospital workflows to function as decision support, aligned with clinical roles and daily routines, rather than as an external tool clinicians needed to learn or manage.
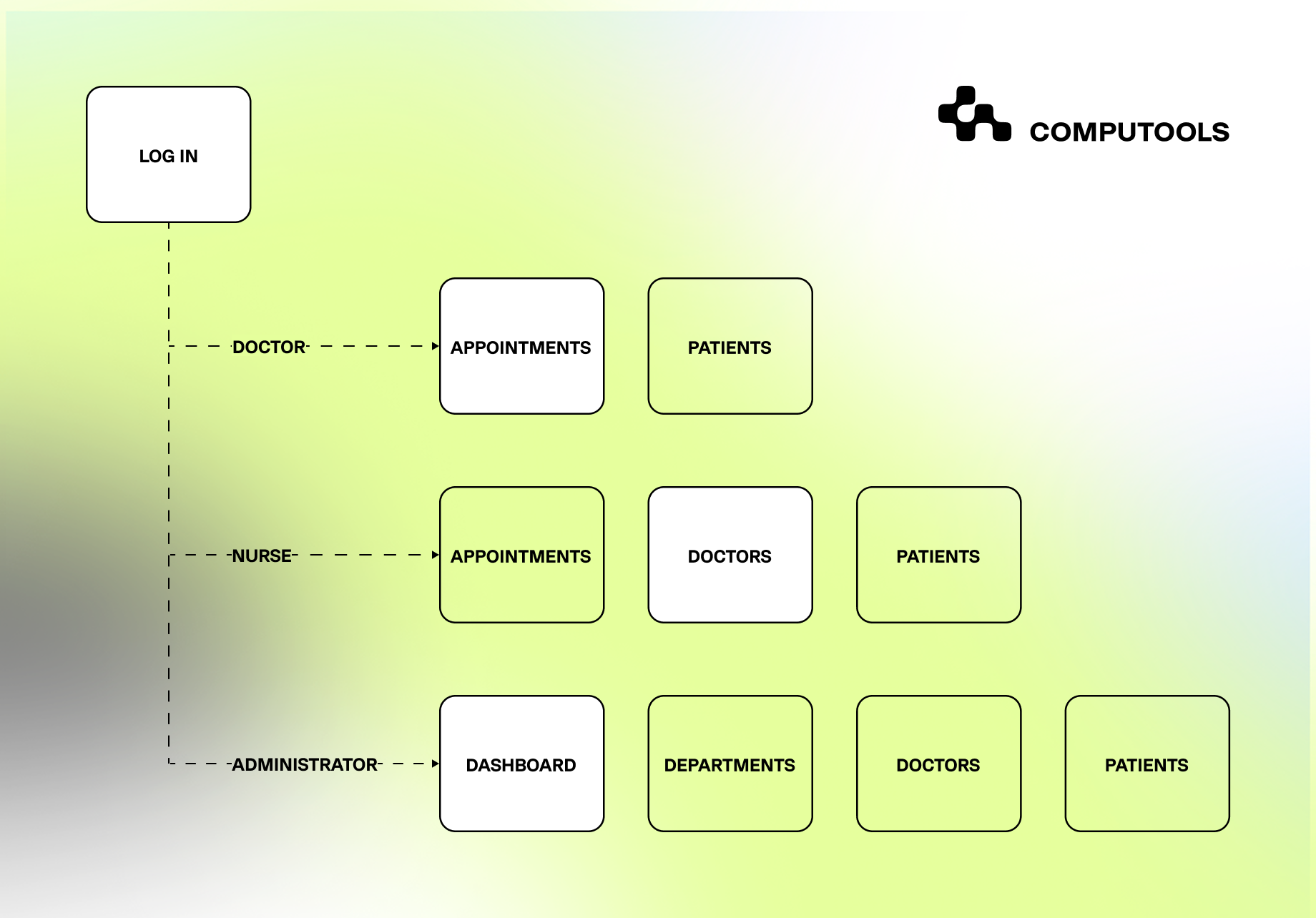
The system was deliberately designed to preserve clinical responsibility. AI outputs supported physician judgment without replacing it, reinforcing trust and ensuring adoption across medical teams. Administrators and support staff accessed aggregated insights relevant to coordination and planning, while physicians received structured diagnostic support at the point of decision-making.
As a result, MediDirect achieved measurable improvements in operational efficiency and diagnostic accuracy while reducing data-related errors. Following the platform’s launch, the company increased its market share in healthcare solutions by 15%, successfully entering a competitive segment with a product that translated advanced AI capabilities into practical, workflow-aligned outcomes.
This case demonstrates a critical principle: in healthcare, AI delivers impact only when it is integrated at the system and workflow level. Model accuracy alone is not enough. Sustainable adoption depends on architecture, data consistency, and alignment with how clinicians actually work.
Healthcare organizations are increasingly turning to intelligent automation to reduce operational strain and improve patient interactions. Read the article “AI Agents in Healthcare Industry: Smarter Automation for Better Patient Experience” to see how AI agents are transforming everyday healthcare workflows without disrupting clinical care.
How to integrate AI diagnostics into existing hospital workflows: a 7-step guide
Step 1. Assess readiness and define goals
Start with a reality check: what data is available, how clean and complete it is, whether your EHR/EMR supports APIs and standards (FHIR/HL7), what security controls already exist, and who will own the change.
Add a baseline (time spent on documentation, reconciliation, no-shows, overtime) so you can prove impact later. This forms the foundation of hospital digital transformation with AI.
In MediDirect, the project began by consolidating fragmented patient metrics and agreeing on a single, consistent calculation approach so teams weren’t making decisions based on conflicting numbers.
Step 2. Identify high-impact use cases
Choose use cases that remove friction at real decision points: triage, medication review, follow-ups, scheduling, documentation, and patient communication. Prioritize by clinical value + operational ROI + feasibility (data access, integration complexity, safety risk), and write down what “good” looks like for each use case before you build anything.
In this way, AI solutions for healthcare providers become deployable, not theoretical. In MediDirect, the scope focused on improving patient assessment and supporting more consistent medication management, and on maintaining complete medical records with clear, role-based access for doctors, nurses, and administrators.
Step 3. Select vendors and tools
Evaluate tools as if integration itself is the product: assess evidence (peer-reviewed where relevant), security and compliance readiness, deployment model (cloud, on-prem, or hybrid), and the ability to fit into existing clinical flows without adding extra clicks.
Run a narrowly scoped pilot, define clear acceptance criteria for accuracy, latency, uptime, error handling, and confirm support for training and change management. This is where AI implementation in healthcare systems most often succeeds or fails in real clinical environments.
At this stage, strong healthtech software development services make the difference between a controlled rollout and an expensive pilot that never scales.
In MediDirect, the solution was built as a centralized platform on a stable stack, including Azure-based storage, enabling AI and analytics to operate on unified data rather than scattered modules.
Step 4. Design workflows and manage change
Map the current workflow end-to-end (including “shadow work” like copying between systems), then design where AI assists: auto-structuring inputs, pre-filling forms, flagging anomalies, summarizing history, or nudging next steps.
Build guardrails (confidence thresholds, clinician confirmation, audit trails) and make feedback loops easy (“useful / not useful/incorrect”) so adoption improves over time, which is the practical core of Clinical workflow automation with AI.
In MediDirect, the platform was designed around different roles and permissions so that insights support daily work rather than forcing clinicians into a separate AI tool.
Step 5. Implement and integrate with existing systems
Treat integration as engineering: data mapping, identity matching, event triggers, retries, fallbacks, and monitoring. Decide which capabilities must be synchronous (real-time suggestions) and which can be asynchronous (background processing), and define what the user sees when AI is unavailable.
This step depends heavily on Interoperability of AI in hospital IT systems, because hospitals rarely run on a single clean data source.
In MediDirect, consolidating disparate data sources into a single system eliminated the need to reconcile patient information across local modules before AI-assisted analysis could be trusted.
Step 6. Measure, evaluate, and scale
You can’t manage what you don’t measure: compare baseline vs. post-launch metrics for documentation time, reconciliation effort, error rates, throughput, patient satisfaction, and financial impact.
Scale only after the pilot is stable, and expand in controlled waves (one clinic/department → multiple → org-wide) with feature flags and rollback plans.
In MediDirect, post-launch results were tied to measurable business traction (including reported market growth), which is the kind of signal stakeholders need before broader rollout.
Step 7. Manage risk, ethics, and governance
Define governance early: who approves model updates, how bias and drift are monitored, how incidents are handled, and what audit evidence is stored.
For diagnostic use, validate on representative data, document limitations, and ensure clinicians retain decision ownership with transparent reasoning and traceability, especially for AI tools for medical diagnostics.
In MediDirect, strengthening data security and standardization reduced the risk of “convincing but wrong” outputs produced from inconsistent inputs.
As healthcare providers seek to improve patient engagement and operational visibility, CRM systems are increasingly central to modern care. Read “Top 12 Benefits of CRM Development for Healthcare Industry” to learn how healthcare CRM solutions boost coordination, retention, and outcomes.
Implementation notes: what actually makes it possible to integrate AI into hospital systems in production
In real hospital environments, success depends less on models and more on execution discipline.
Healthcare data integration with AI starts with strict control over data contracts: every input must have a defined owner, version, validation rules, and traceability across systems. Without this, even accurate models produce inconsistent outputs once workflows scale.
• Versioning is critical. AI components should be deployed with clear model registries, rollback mechanisms, and feature flags, allowing teams to test improvements safely without disrupting clinical operations. Latency budgets must be defined upfront so clinicians know when to expect AI support and what happens when it’s unavailable.
• Auditability is non-negotiable. Every AI recommendation should be traceable back to the source data, logic, and model version. This protects clinical teams, supports compliance reviews, and builds long-term trust.
Finally, production-ready AI-driven diagnostics platforms are designed to degrade gracefully. When confidence is low, data is incomplete, or systems are under load, the platform must default to standard workflows rather than forcing uncertain automation. This balance augmentation, without dependency, enables AI to scale responsibly in healthcare.

See how a well-architected AI diagnostics integration can reduce clinical bottlenecks, support faster diagnoses, and elevate patient experience at scale.
Common integration failure modes (and how to avoid them)
When teams attempt to integrate AI into hospital systems, most failures are not caused by weak models but by predictable integration mistakes. Below are the most common ones and how to avoid them.
1. Broken identity mapping. Patient, visit, or provider identities don’t match across systems, leading to AI insights being attached to the wrong context. This is avoided by defining a single source of truth for identifiers and enforcing reconciliation rules before AI is applied.
2. Mismatched clinical definitions. The same metric (e.g., “active medication” or “recent visit”) is defined differently across modules. AI trained on one definition produces outputs that contradict another. The fix is to standardize clinical definitions at the data layer, not within individual models.
3. AI introduced outside real workflows. Insights are presented in separate dashboards or reports that clinicians rarely open. Adoption drops to zero. AI must be embedded within existing tools at the exact moment a decision is made.
4. Over-automation without guardrails. Systems automatically act on AI outputs, even when data is incomplete or confidence is low. This creates risk and erodes trust. Production systems must enforce human confirmation, confidence thresholds, and safe fallbacks.
5. No observability or audit trail. Teams cannot explain why an AI recommendation was generated, which data it used, or which model version produced it. This is especially dangerous for AI diagnostics integration, where traceability is mandatory for trust, compliance, and incident review.
6. Ignoring performance constraints. AI responses are slow, unpredictable, or fail silently under load. Clinicians stop relying on them. Defining latency budgets, timeout behavior, and graceful degradation is essential.
7. Scaling before proving value. AI is rolled out broadly before outcomes are measured. When results disappoint, rollback becomes politically and technically difficult. Always pilot first, measure impact, then scale deliberately.
Most teams discover that the real challenges of integrating AI into hospital clinical workflows emerge only after deployment, when misaligned data, broken handoffs, and everyday clinical realities push back against elegant designs.
Global leaders in AI integration: real-world examples
Some of the most advanced healthcare organizations demonstrate that successful AI diagnostics integration depends on embedding intelligence directly into clinical operations rather than deploying isolated tools.
A prominent example is Mayo Clinic, where AI-driven diagnostics are integrated into radiology, cardiology, and pathology workflows. Mayo focuses on delivering insights within existing clinical systems, ensuring diagnostic support is available exactly where clinicians make decisions.
A similar model is followed by the Cleveland Clinic, which deploys AI for imaging analysis and predictive diagnostics while maintaining strong clinical ownership and oversight. These initiatives reflect best practices for integrating AI diagnostics into hospital workflows, where adoption is driven by usability, explainability, and seamless workflow alignment rather than model novelty.
On the technology enablement side, Epic Systems plays a critical role in large-scale medical AI software integration. Instead of acting as an AI vendor, Epic provides native EHR frameworks that allow healthcare providers to run validated AI models within the clinical record. This approach ensures diagnostic signals are contextual, traceable, and governed by existing clinical processes.
In diagnostic imaging, Siemens Healthineers and GE Healthcare have embedded AI directly into the imaging platforms radiologists use daily. Their solutions prioritize reproducibility, regulatory readiness, and interoperability with hospital IT ecosystems, demonstrating how AI can scale without disrupting established diagnostic routines.
Across these organizations, governance is treated as infrastructure rather than policy. Formal lifecycle controls, auditability, bias monitoring, and accountability frameworks are embedded in deployment models and increasingly supported by dedicated AI governance services to ensure safety, compliance, and long-term trust in clinical environments.
Healthcare providers increasingly rely on specialized software partners to drive digital transformation. Read “Top 25 Healthtech Software Development Companies in 2026” to see which companies are leading the market.
Why healthcare providers choose Computools
Computools has built and scaled production-grade healthcare software for over 12 years, working with hospitals, clinics, pharmacies, and healthtech companies across the US, EU, Middle East, and Asia.
Proven Healthcare Delivery at Scale
• 250+ engineers with dedicated healthcare domain expertise
• 20+ healthcare projects delivered globally, including hospital platforms, AI-enabled diagnostics, EHRs, and workflow automation
• ISO 9001 / ISO 27001 certified, fully HIPAA & GDPR compliant
• 4.9 rating on Clutch based on 78+ verified client reviews
These figures reflect systems used daily by medical professionals in real clinical environments where reliability and speed directly impact patient outcomes.
Computools specializes in custom hospital software development, creating platforms that integrate seamlessly with existing clinical workflows rather than forcing hospitals to adapt to generic tools. This approach enables modernization without disrupting care delivery or increasing operational risk.
Healthcare organizations working with Computools achieve tangible results: faster access to patient data for time-critical decisions, reduced administrative costs through workflow automation, and fewer errors caused by fragmented or inconsistent records. Centralized architectures improve care coordination while easing the burden on clinical and administrative staff.
A key differentiator is deep expertise in healthcare AI system integration. AI-driven diagnostics and analytics are embedded directly within hospital IT ecosystems, ensuring governance, auditability, and long-term scalability, rather than relying on isolated, hard-to-maintain AI tools.
Computools’experience is proven in production. In Israel, the company delivered an AI-powered dental healthcare platform that processes medical images and generates diagnostic reports in seconds.
In the US, an RFID-based medical equipment tracking system increased client revenue by 56% and reduced checkout time by 74%, improving both efficiency and patient safety.
Have a healthcare or AI integration project in mind? Email us at info@computools.com to discuss your requirements and get a project estimate.
Conclusion
Integrating AI into hospital workflows has evolved beyond experimentation; it now focuses on developing reliable systems that enhance accuracy, speed, and trust in everyday clinical operations. When AI is embedded in existing processes, aligned with real workflows, and properly governed, it becomes a practical tool for reducing clinician burden and improving patient outcomes.
Successful implementations focus on data quality, interoperability, workflow alignment, and measurable results. In this context, AI-powered clinical decision support is most effective when integrated into a unified, production-ready healthcare platform that clinicians can depend on in real-world settings.
Computools
Software Solutions
Computools is an IT consulting and software development company that delivers innovative solutions to help businesses unlock tomorrow.








“Computools was selected through an RFP process. They were shortlisted and selected from between 5 other suppliers. Computools has worked thoroughly and timely to solve all security issues and launch as agreed. Their expertise is impressive.”