Warehouses are evolving into hybrid and autonomous centers: dark warehouses fully robotic facilities without human presence are now part of the operational models such as Amazon, Ocado, and DHL, showcasing efficiency at scale today, not in the future.
In 2023, the global warehouse automation market was valued at $19.23 billion and is projected to reach $59.52 billion by 2030, at a CAGR of 18.7%. The fastest-growing segments include mid-level automation (from $9.4 billion in 2024 to $26 billion in 2030, CAGR ≈ 19.8%) and fully autonomous warehouses (from $1.17 billion in 2024 to $3.43 billion in 2030, CAGR ≈ 21%).
The broader logistics automation market, which includes warehouse processes, is expected to grow from $34.6 billion in 2023 to $90 billion by 2030 (CAGR ≈ 15%).
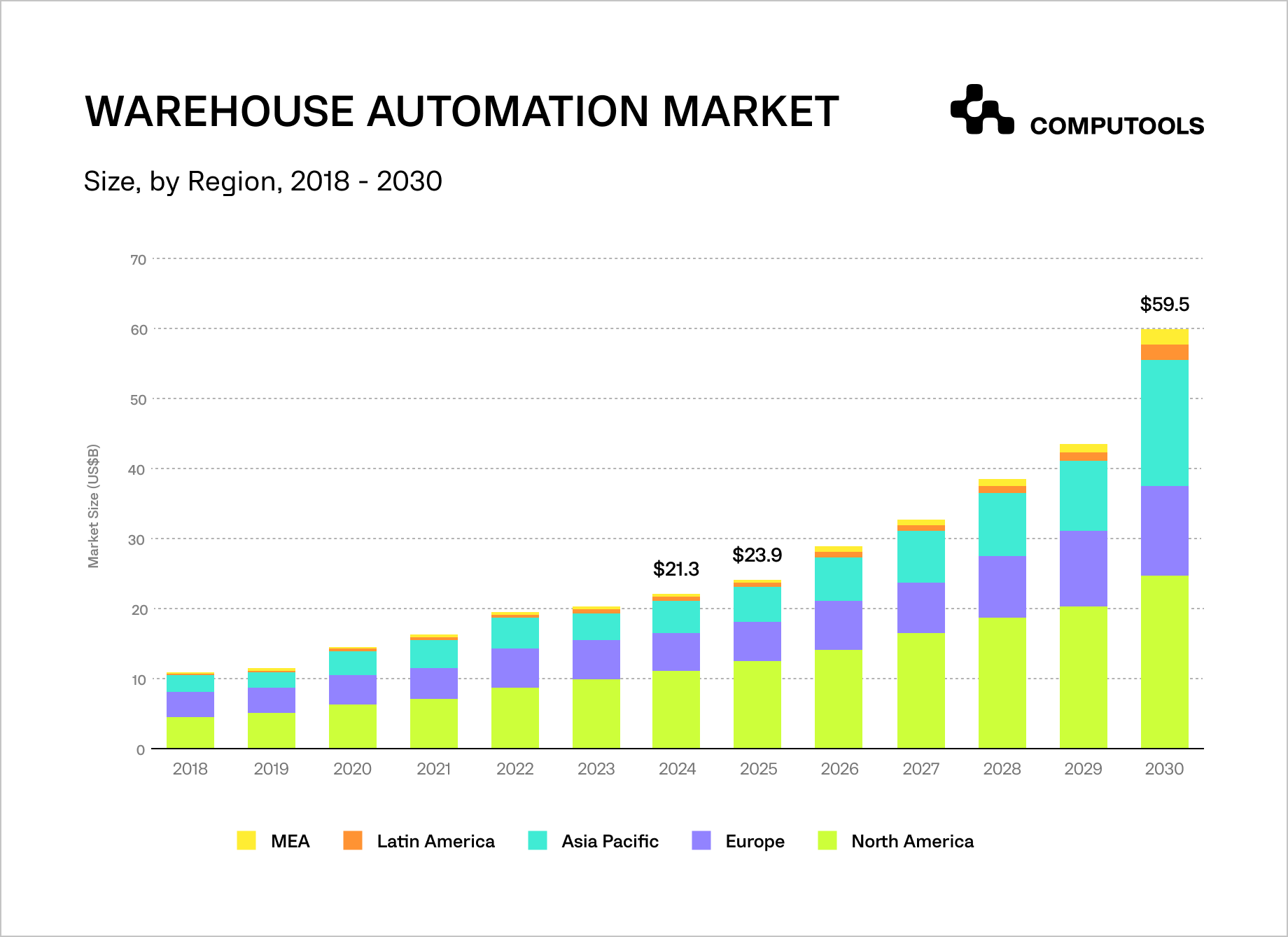
Europe mirrors this growth trajectory. The European warehouse automation market stood at $6.8 billion in 2023 and is forecast to double to $13.7 billion by 2030 (CAGR ≈ 10.1%).
Western Europe leads with over 40% market share, driven by strong adoption in Germany, France, the UK, and the Netherlands. At the same time, Eastern Europe accelerates due to e-commerce expansion and new logistics hubs.
Key growth drivers include:
• The e-commerce boom requires faster and more accurate order fulfillment.
• Labor shortages and rising operational costs across major economies.
• The need for resilient supply chains after global disruptions.
Core processes from receiving and sorting to storage, picking, and shipping are now driven by AS/RS systems, AGVs/AMRs, robotic arms, conveyor automation, and other warehouse robotics solutions. This achieves accuracy rates of up to 99.9% and reduces labor needs by as much as 60%.
A vivid example of this trend is Walmart’s move into large-scale automation. In 2023, the retail giant unveiled its first fully automated 1.4 million-square-foot distribution center in Brooksville, Florida. This milestone came just a year after Walmart acquired a minority stake in Symbotic, a warehouse technology company.
The facility now has fleets of robots, self-driving forklifts, and advanced sorting systems, significantly increasing throughput without reducing staff. Instead, human workers are reassigned to higher-value tasks like deliveries.
Walmart’s approach reflects a wider industry outlook: automation isn’t just about saving money, but also about boosting capacity, speed, and operational resilience.
What is warehouse automation in 2026?
Warehouse automation uses advanced technologies and systems to streamline and optimize various processes in a warehouse. Automation technology has the potential to reduce labor costs by up to 60%, increase labor productivity by 30%, decrease errors by up to 99%, cut shipping and handling times by up to 50%, and boost warehouse storage capacity by up to 50%. It can also reduce operational costs by up to 30%.
The warehouse automation market has experienced significant growth in recent years as companies across industries recognize the benefits of automating their supply chain operations.
The demand for warehouse automation solutions is driven by faster order fulfillment, rising labor costs, increasing customer expectations for rapid and accurate deliveries, and the desire to improve overall operational efficiency.
Types of automation by technological approach
Warehouse process automation involves tools, technologies, and digital solutions that assist in managing the warehouse, including digital and physical automation.
• Digital automation involves advanced warehouse management systems (WMS) that go beyond inventory and order tracking. Modern WMSs increasingly integrate WCS features that help coordinate the activities of automated equipment in real time for smoother operations.
These advanced systems combine traditional WMS solutions and WCS capabilities for more integrated and efficient warehouse management.
• Physical automation involves moving and handling goods, using automated guided vehicles, conveyor belts, robotics, and automated picking systems.
These solutions help automate processes like moving goods, sorting, and packaging, reducing the need for manual labor and considerably speeding up warehouse operations.
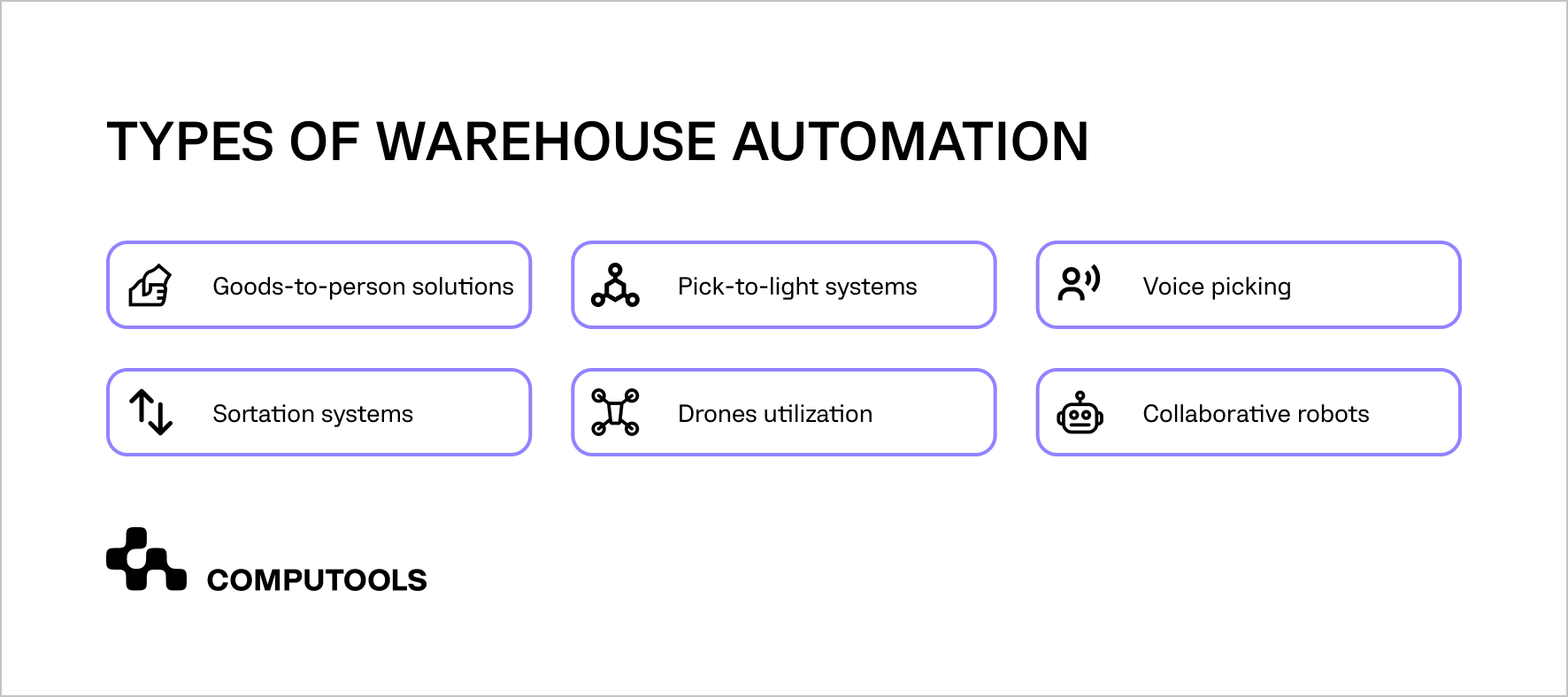
Types of automation by technological solution
• Goods-to-person solutions: Systems that bring inventory directly to warehouse workers, reducing travel time and increasing picking efficiency.
• Pick-to-light systems: Light-directed picking technology guides operators to the correct items quickly and accurately.
• Voice picking: Hands-free picking, guided by voice commands, improves speed and reduces picking errors.
• Sortation systems: Automated systems that classify and route products to their appropriate locations.
• Drone utilization: Drones are used for rapid inventory checks and inspections, especially in extensive facilities.
• Collaborative robots (Cobots): Robots designed to work alongside humans, handling repetitive or heavy tasks while employees focus on more complex activities. Robots may replace 40% of warehouse jobs by 2030.
This combined approach gives businesses a clear framework for choosing the right automation strategy, whether upgrading warehouse automation software, deploying automated guided vehicles in warehouses, or integrating specialized solutions for specific operational needs.
Levels of automation
The automation of the warehouse can be categorized into three primary levels, depending on the extent of technology adoption and process integration.
1. Low-Level Automation (Basic Automation)
This stage focuses on improving manual operations with handheld barcode scanners, basic conveyor belts, forklifts, and entry-level warehouse management systems to help streamline operations.
While processes remain largely manual, this level improves inventory visibility, reduces human error, and speeds up order processing.
2. Medium Automation (Partial Automation Stage)
This stage integrates industrial automation solutions such as conveyor systems, sortation systems, and automated guided vehicles in warehouses.
Operators work alongside automated equipment to improve throughput and reduce physical strain, making it ideal for warehouses handling high volumes with variable demand.
3. High Automation (Fully Automated Stage)
Most operations are performed by advanced systems like AS/RS (Automated Storage and Retrieval Systems), robotic arms, and AI-powered warehouse automation software.
This enables “dark warehouses” where minimal or no human presence is required, achieving maximum efficiency, accuracy, and scalability. Examples include Amazon Robotics facilities and Ocado’s fully automated fulfillment centers.
Which tasks in a warehouse can be automated?
Today, warehouse intelligent automation can transform nearly every stage of operations, from when goods arrive to when they leave for delivery.
Below are the core processes most commonly enhanced with advanced technology:
1. Inbound processing and put-away. Automated scanners instantly register incoming goods into the company’s inventory management system, ensuring immediate visibility and minimizing human error.
2. Order picking. Autonomous Mobile Robots (AMRs) and smart automated picking systems can locate and collect products quickly, significantly reducing staff travel time across the facility.
3. Packing operations. Intelligent packing stations automatically scan, weigh, and size items, selecting the most efficient packaging materials to optimize costs and sustainability.
4. Staging areas. Conveyor lines and AMRs transfer goods to designated loading areas, streamlining pre-shipment preparation.
5. Loading automated guided vehicles (AGVs), conveyors, and robotic arms load pallets or individual parcels into trucks, improving speed and consistency.
6. Cross-docking. Using warehouse sortation systems, conveyors, and RFID technology, products can be redirected to outbound docks without long-term storage, cutting handling times.
7. Internal transfers. Autonomous vehicles efficiently move items between storage areas, processing lines, and workstations.
8. Automated quality control. Computer vision tools scan items to detect defects, damages, or irregularities in seconds, ensuring compliance with quality standards.
9. Outbound sorting and shipping. High-speed sortation systems with barcode scanners arrange goods according to shipping method, route, or delivery priority.
10. Inventory tracking. RFID and IoT sensors monitor stock levels in real time, sending alerts when replenishment is required and triggering auto-restocking processes.
11. Returns handling. Automated conveyors and scanners quickly categorize returns for repackaging, refurbishment, or reintegration into stock.
12. Production-linked warehousing. In facilities connected to manufacturing, AGVs, AMRs, and industrial robots support tasks such as material movement, assembly, painting, welding, and packaging.
Benefits, challenges, and solutions of warehouse process automation
| Benefit | Challenge | Solution |
| Reduced errors in warehouse operations. Automation minimizes human mistakes in tracking, picking, and shipping, improving accuracy by 15–25% (AS/RS + IoT) and boosting customer satisfaction. | Inventory shrinkage & damage control losses due to theft, damage, and administrative errors distort stock visibility. | Warehouse automation software with real-time inventory tracking, RFID integration, AI-enabled demand forecasting, and security system integration. |
| Improved efficiency in order processing. Streamlined workflows speed up fulfillment, reducing delays and increasing productivity by up to 35% | Order fulfillment issues include picking, packing, shipping errors, slow delivery, and increased returns. | Pick-to-Light and voice picking systems, optimized picking routes, wave/batch picking, and last-mile delivery integration. |
| Increased adaptability and productivity. Automation enables quick adjustments to changes in demand without compromising performance. | Seasonal demand fluctuations result in stockouts in peak periods and overstocking in low-demand seasons. | AI-powered forecasting, historical sales analysis, AI predictive analytics, dynamic goods distribution, and on-demand warehousing. |
| Reduced costs and reliance on manual labor. Automated picking and sorting can cut labor costs by 20–30% and lower workplace injuries by 40%. | Labor shortages & workforce retention difficulty hiring and keeping skilled staff for repetitive tasks. | Automating repetitive warehouse process automation tasks, workflow optimization, integration with AGVs, robotics, AS/RS, and improved employee training. |
| Operational flexibility and scalability. Ability to quickly adjust capacity for changing market needs, including reverse logistics | Complexities in reverse logistics, such as inefficiently handling returned goods, cause delays and customer dissatisfaction. | Automated returns processing, RMA management, automated return labels, real-time tracking of returned items, and integration with customer service. |
| Optimized space utilization. Automation allows smarter use of vertical and horizontal warehouse space. | Limited warehouse space utilization, poor layout, underused capacity, and slow operations. | Warehouse layout optimization tools, slotting optimization, support for vertical storage, and cross-docking |
| Better long-term ROI. Optimized workflows and accuracy improvements lead to faster payback despite high upfront costs. | High initial costs & integration complexity, advanced systems like AS/RS require significant investments and may not align easily with legacy software. | Phased implementation, hybrid automation models, middleware for integrating legacy WMS with modern systems, and ROI-focused automation roadmaps. |
When should a logistics business consider automation of the warehouse?
Several signs and prerequisites signal that your warehouse is no longer operating at full capacity, and it is time to consider implementing warehouse software and other technologies:
1. Growing order volume without a proportional increase in staff. If the number of operations is growing, but the workforce is not enough, automation can help cope with the load without the additional cost of constantly hiring staff.
2. High error rates in picking and shipping. Frequent errors in order picking or incorrect labeling lead to returns, additional costs, and reputational damage. Automated systems minimize these risks.
3. Difficulties with real-time inventory tracking. If inventory takes days and information about balances is often inaccurate, automated solutions can provide precise control and quick access to data.
4. Uneven peak loads. Seasonal sales, promotions, or large orders create “bottlenecks” in processes. Automation allows you to quickly scale operations without losing speed and quality.
5. Limited space and inefficient use of space. Automated storage systems will help optimize vertical space by increasing storage density without expanding the warehouse.
6. High operating costs. If the costs of salaries, processing, and warehouse maintenance are steadily increasing, automation allows you to reduce them by optimizing processes and reducing the share of manual labor.
Therefore, implementing effective logistics automation approaches helps eliminate existing bottlenecks and sets the stage for scalability, enhanced accuracy, and increased stability across all warehouse operations.
Step-by-step planning: preparation and implementation of automation
Implementing automation is a strategic process that requires a comprehensive approach and realistic supply chain planning. Successful automation through advanced technology and teamwork, transforming the warehouse into an efficient and high-performance center.
1. Assessing the need and defining goals
Before you start, analyze the challenges of your warehouse: order fulfillment speed, inventory accuracy, and staff workload. Introduce existing audit processes, infrastructure, and software to ensure the optimal level of automation.
2. Choosing warehouse automation solutions
Choose automation software and other tools that easily integrate with your warehouse management system (WMS) and ERP. It is crucial that the solution is scalable, flexible, and supports warehouse process automation functions.
3. Pilot launch
Start with partial automation, for example, automate inventory, order picking, or packaging. This approach reduces financial burdens and allows you to test new processes without risk to the entire system.
4. Team training
Provide personalized training and instructions on how to use new systems. Open communication channels, adapt quickly, and avoid mistakes at the start.
5. Automation scaling
Gradually implement additional modules and technologies, focusing on data from pilot projects. Use real-time analytics to track KPIs and optimize processes.

Explore how warehouse automation transforms fulfillment speed, labor efficiency, and inventory accuracy—and assess what it would take to modernize your operations.
Key features to look for in warehouse automation systems
• Seamless integration with existing systems. Easy integration with WMS, ERP, and other logistics tools for real-time data synchronization and effective inventory management.
• Scalability and flexibility. Ability to expand functionality and adapt the system to the needs of a growing business.
• Advanced inventory management. Using RFID, barcode scanning, and AI-based demand forecasting for inventory accuracy and error reduction.
• Automated picking and packing. Robotic manipulators, pick-to-light, and voice-directed picking to speed up processes and increase accuracy.
• Analytics and real-time data. AI-based analytics, monitoring efficiency, and forecasting warehouse needs.
From AI to robotics: trends for 2026 and beyond
The rapid adoption of advanced technologies drives the future of the warehouse.
• Machine learning in warehouse automation enables more intelligent decision-making, cost reduction, and predictive maintenance by analyzing large volumes of operational data.
• Warehouse robotics trends show a clear shift from AGVs to more intelligent Autonomous Mobile Robots (AMRs), which offer flexible navigation, real-time inventory scanning with RFID, and scalable material handling.
• IoT devices are becoming standard, allowing real-time inventory flow tracking, monitoring, and optimization.
• Sustainability is shaping system design, focusing on eco-friendly, energy-efficient solutions.
• Collaborative robots (cobots) are increasingly integrated into workflows, combining human dexterity with automation efficiency.
• AI-powered systems optimize order routing, demand forecasting, and predictive maintenance, reducing downtime by up to 30%.
• Machine learning algorithms improve inventory accuracy and reduce stockouts.
Adopting intelligent automation for warehouse sorting systems enables faster, more accurate, and scalable operations. These trends transform warehouses into highly efficient, connected, and environmentally responsible hubs.
By 2030, industry analysts expect robots to handle up to 40% of existing warehouse jobs, transforming labor structures and skill demands. Early adopters of automation will secure a competitive advantage by enabling faster order fulfillment, reducing operational costs, and improving scalability.
Conversely, companies that postpone implementation may fall behind in a supply chain that is becoming more data-driven and automated.
Partner with Computools for next-generation warehouse solutions
Computools delivers cutting-edge warehouse software development services that transform logistics operations into efficient, scalable, and data-driven ecosystems. With proven warehouse management software development expertise and strong cases in the logistics sector, we create intelligent, fully integrated solutions from AI-powered analytics to IoT-enabled monitoring and robotics.
Our track record includes projects like HubMarine, a platform that optimizes vessel placement, berth booking, and marina navigation across 100+ marinas worldwide.
Leveraging machine learning and IoT, the solution reduced communication and pre-booking time by 75%, improved transparency, and increased operational efficiency. These same logistics automation approaches drive measurable results in warehouse environments.
Our team understands the unique challenges of supply chain and warehouse automation, ensuring seamless integration, maximum efficiency, and measurable ROI. Partnering with Computools means gaining a powerful ally in your pursuit of success.
Let’s discuss how we can accelerate your warehouse automation and give you a competitive edge. Contact us at info@computools.com.
Computools
Software Solutions
Computools is an IT consulting and software development company that delivers innovative solutions to help businesses unlock tomorrow.








“Computools was selected through an RFP process. They were shortlisted and selected from between 5 other suppliers. Computools has worked thoroughly and timely to solve all security issues and launch as agreed. Their expertise is impressive.”