Energy companies frequently deal with problems including resource management, capital planning, operational risks, supply and demand swings, and commodity market cyclical volatility.
However, they are now using a new tool called artificial intelligence in the energy market to address the long-standing requirement to make better and more efficient judgments in the energy transition period.
AI in the energy industry is changing it and transforming the production, distribution, management, and final use of energy from conventional to renewable sources. In many respects, power production corporations were early adopters of AI-based energy systems and have since gradually shifted to it for their next-generation systems.
The growing demand for increased throughput, operational efficiency, and sustainability is propelling implementation.
Statista researched the compound annual growth rate of the AI energy market worldwide from 2019 to 2024 and suggested dividing it by region:
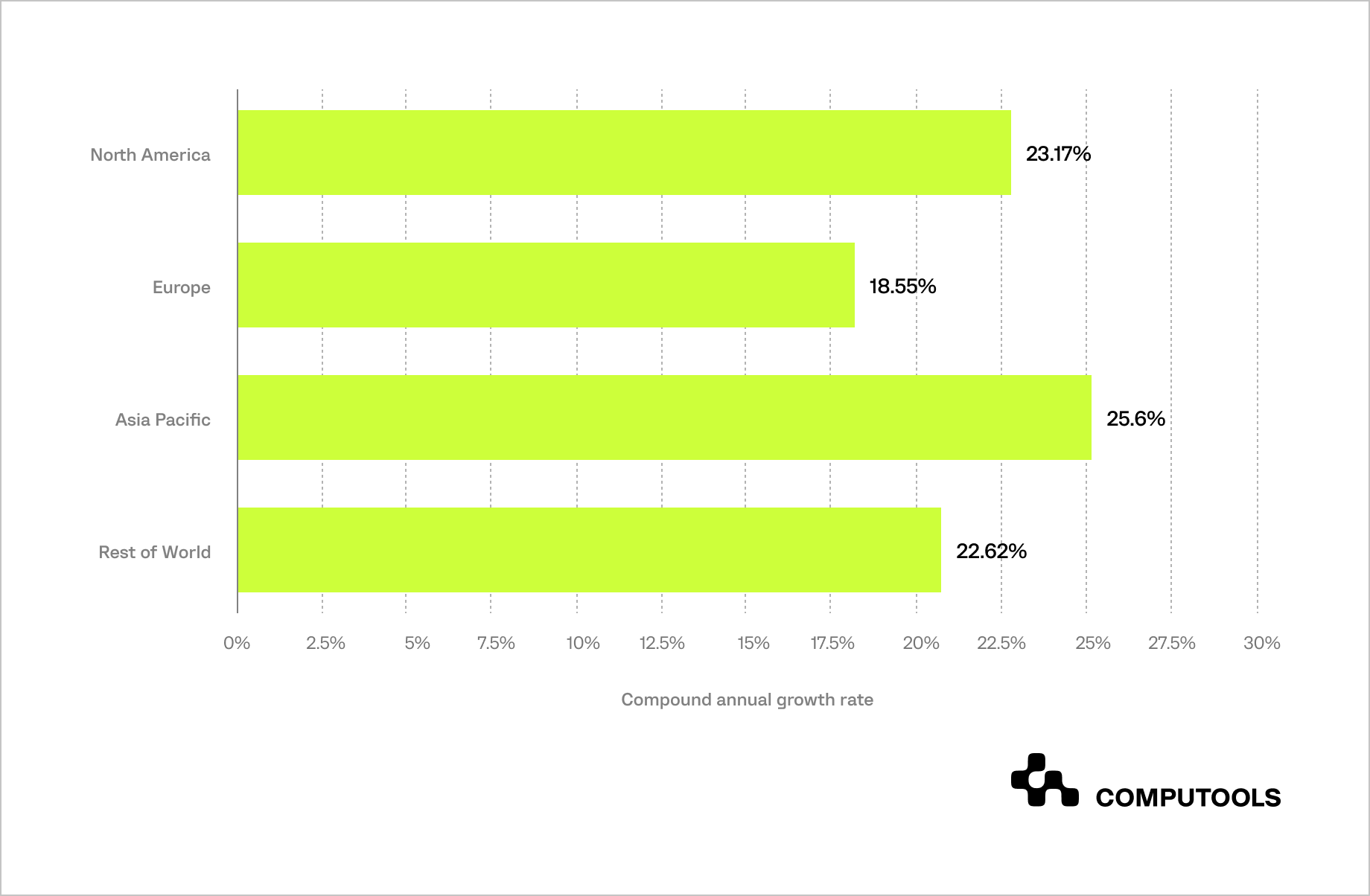
Investments in AI technologies have soared, with global spending on AI software for energy in the energy sector projected to reach $7.78 billion in 2024.
The AI market in the Asia Pacific region alone is expected to grow at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 25.6%.
Benefits Of AI in the Energy Industry
There is much that stands to gain when AI energy solutions are integrated into the energy sector. By building these advantages, energy companies will be able to manage the transition toward a new, more efficient organisation model, which will deliver a green and economically secure power industry.
1. Operational Efficiencies
One of the benefits of AI in the energy industry is optimising the value chain. AI means that large amounts of information from various sources can be assessed and help energy companies provide energy such as generation and distribution.
In another way, by applying analytical approaches, ML in the energy sector can identify potential equipment issues that may lead to failure, thus enabling maintenance actions in advance and decreasing performance and time lost expenses.
Furthermore, using AI-based energy solutions in work processes makes it easy to automate most activities, allowing human beings to focus on more important work.
2. Enhanced Demand Prediction
AI in energy management is used in demand management, and since demand is an aspect integral to managing energy resources, it is central. AI can predict consumption patterns better with the help of historical data and the real-time inputs fed into it.
This capability enables suppliers in the energy industry to make necessary corrections to supply so that their supply is not far from the demand.
Consequently, this results in utilising available resources more efficiently, reducing operational costs.
3. Sustainability Initiatives
AI enhances sustainability policies that are extensively applied to the energy field. AI can further help manage renewable energy to a great extent as energy generation from renewable sources such as solar and wind is intermittent, and it’s difficult to predict when they will be able to generate maximum or minimum amounts of electricity.
This helps increase the grid’s stability level and promotes renewable energy in current systems. In addition, AI is useful for monitoring and decreasing carbon emissions since the technology can reveal energy waste tendencies and propose improvement changes.
4. Risk Management
AI software development helps the energy sector minimise and manage risks within the organisation. With the help of analytics, AI can predict and prevent risks related to infrastructure, like climate or system weaknesses.
This capability is important to protect the global energy supply chain because this domain or network is more easily attacked by compound factors such as cyber threats and natural disasters.
5. Cost Reduction Strategies
Adopting AI has deeper financial impacts. For instance, AI development services can be useful in cutting operation expenditures and managing constraints, enabling energy firms to save a great deal.
For instance, AI findings can be applied in demand response management, which involves the execution of management activities that control the amount of electricity consumed in companies and homes in certain time periods to reduce costs.
Furthermore, with a deep understanding of patterns, mistakes, and coming tendencies, the finances can be planned and resources – invested more effectively.
AI Use Cases in the Energy Industry
There are currently at least six types of potential AI energy solutions use within the energy industry. Let’s see what they are:
1 Renewable Energy and Power Generation
• Grid Management: AI helps optimise the distribution and stability of energy across grids. Autogrid Flex uses machine learning to predict grid fluctuations and optimise energy distribution across large networks.
• Energy Storage: AI-driven systems improve the efficiency and capacity of energy storage solutions. Stem’s Athena Platform leverages AI to manage energy storage systems by analysing usage patterns and maximising battery efficiency.
• Smart Infrastructure: AI supports residential and commercial real estate power supply infrastructure. Siemens MindSphere integrates AI for managing smart grids in residential and commercial buildings, ensuring efficient energy distribution and reduced waste.
• Forecasting Supply and Demand: AI forecasts the demand for and production of renewable energy. AWS Forecast assists utilities in efficiently planning and allocating resources by predicting energy demands and renewable output using time-series forecasting.
• Nuclear Power Plant Monitoring: AI-powered nuclear power plant monitoring keeps an eye on safety and operations.
Businesses such as EDF Energy use neural network monitoring systems to examine sensor data in order to identify irregularities and enhance nuclear plant safety procedures.
• Carbon Capture, Utilisation, and Storage (CCUS): AI improves technology for carbon capture, utilisation, and storage (CCUS).
By constantly modifying settings in response to real-time plant data, Carbon Clean’s AI systems maximise the effectiveness of carbon capture operations.
2. Asset Management and Maintenance
• Reducing Downtime: Some examples of AI are “digital twins”, a virtual replica of the physical system to increase availability by reducing the likelihood of system failure.
GE’s Predix Digital Twin real-time categorisation of industrial assets encompasses the capability to predict failure modes and recommend preventive actions.
• Defect Detection: AI captures problems with equipment before developing into other severe forms. The AI-based Asset Intelligence Platform from Uptake detects equipment failure opportunities before it poses a problem.
• Asset Tracking: AI enhances the daily management and tracking of physical assets in several ways. IBM Maximo leverages AI to determine equipment’s status and performance history to improve functionality.
3. Health, Safety, and Training
RemoteSpark by Kognitiv Spark offers workers training and on-the-job support via augmented reality, underlain by machine learning.
AI Aatmunn by Guardhat identifies potentially hazardous situations and sends warnings to employees and managers to improve workplace safety.
4. Operational Efficiency
• Inventory Management and Procurement: AI improves the management of stock control and supply chain management.
SAP’s Integrated AI Suite decreases the procurement cycle through inventory need forecasting and supply chain streamlining.
• Optimised Logistics: AI enhances logistics for faster and more efficient energy delivery.
C3 AI Supply Chain Suite streamlines logistics for energy distribution by predicting delivery delays and optimising routes.
• Back-office Optimisation: AI streamlines administrative and operational tasks. UiPath’s AI Automation Tools automate repetitive administrative tasks, freeing up human resources for strategic activities.
5. Cybersecurity
• Real-time Breach Detection: AI identifies and resolves security breaches as they occur. Darktrace Enterprise Immune System uses AI to detect and neutralise cyber threats as they occur in real-time.
• Vulnerability Assessment: AI pinpoints weaknesses to prevent future breaches. Qualys AI Cloud Platform analyses systems to pinpoint vulnerabilities and recommend protective measures.
• Improved Security Protocols: AI develops strategies to minimise risks, even though no system is entirely foolproof.
Palo Alto Networks’ Cortex XDR uses AI to continuously adapt and develop robust cybersecurity protocols.
6. Project Development
• Brownfield and Greenfield Projects: AI optimises designs and solutions for both existing sites (brownfield) and new developments (greenfield).
Bentley Systems’ OpenUtilities uses AI to design optimal layouts for new projects and enhance existing infrastructure.
• Faster Turnaround: AI accelerates project timelines. Building AI by nPlan forecasts project timelines and suggests ways to accelerate construction schedules.
• Enhanced Productivity: AI creates more productive and efficient facilities. Autodesk BIM 360 employs AI to optimise workflows and improve productivity during the project lifecycle.
Regulatory Aspects of AI in the Energy Industry
AI policies and guidelines for the energy industry are being set worldwide to promote AI’s safe use and integration.
In Europe, the EU AI Act targets socially responsible regulation of AI in energy systems and fosters the EU vision of innovation with responsibility.
Internationally, ISO 50001 is being implemented to embed AI technologies to manage energy efficiently, effectively, and compliantly.
Thus, data protection legislation, such as GDPR and other comparable and imminent global rules, is paramount for protecting safe data transmission in AI systems, thereby ensuring the trust and transparency of the applications.

Predictions for AI Use In the Sector
We have reviewed Forbes’s potential predictions of change in various aspects of energy production, distribution, and consumption.
Recent articles stress the focus on the tendencies and innovations in this sphere that AI is expected to bring.
1. Market Investment
The energy market for artificial intelligence is expected to be large, and we predict it will reach as high as about 13 billion in the future.
This strong market growth is driven by the rising funds allocated for the development of AI from oil and gas companies; more than ninety per cent of such companies disclose their investment in AI advancements.
2. Innovations
The application of artificial intelligence in the energy sector is likely to be pursued aggressively ahead of the rest as it is believed this aspect will enhance the optimal functioning of the energy sector.
For example, speech recognition prognosticates as a mainstream strategy, allowing organisations to predict when machines require servicing, thereby minimising outage time.
Furthermore, applying AI technologies will also optimise resource utilisation processes by supporting automated tasks and leaving more important issues to human resources.
3. Renewable Energy
The use of renewable energy sources is expected to grow even further due to AI’s abilities to help manage renewable energy in existing energy networks.
AI will help manage the flow of renewable resources, as the technology will ensure better predictions of energy needs and resource availability, especially for unconventional power suppliers, including solar and wind power.
4. Customer Engagement
AI is also thought to revolutionise customer relations, specifically in the energy market. The use of smart technologies held by artificial intelligence will improve the reaction to consumer interactions, providing clients with real-time data on their energy usage and habits.
This not only enlightens the consumer to make improved choices regarding energy but also improves efficiency by reducing energy use by households and companies.
When it comes to the proactive deployment of these advanced artificial intelligence technologies, a new model of energy infrastructure that will meet people’s needs in the future is possible.
These changes are key to preparing energy companies for the many headwinds of change involved in the transition to the green economy.
Challenges in Achieving Digital Value in the Energy Industry
1. Overcoming Physical Barriers
The energy industry is subject to physical constraints like geophysics, quantum physics, fluid dynamics, thermodynamics, and electromagnetics.
Like most international oil companies, its operation involves central fixed installations such as power plants, offshore platforms, and pipelines, which are expensive. To achieve these things, digital applications must overcome these physical challenges and maintain the front line’s assets, health, and capability.
As for what technologies are fitted into such stringent workflows, they must present value and demonstrate their worth for integration into those processes.
2. Navigating Health and Safety Regulations
Energy, on which people’s lives depend dramatically nowadays, has risks. Still, errors happen. The industry is subjected to several regulations at the local, state, and federal levels, as well as at the international level.
This regulation pressure encourages risk management and reliance on details and rigorous procedures that, in essence, slow the industry down as it cannot embrace change.
3. The Engineer-Led Mindset
The power relations of this physically oriented and regulated industry are led primarily by engineers. This engineer-orientated culture emphasises large-scale, well-articulated projects, a high degree of formal analysis, and perfectionism rather than flexibility and speedy decision-making.
This mentality is not in sync with the experimental approach characterising most digital transformations.
4. Depending on the Complex Supply Chain
The licenses depend on a maze of supply chains involved in energy production, processing, and distribution.
For instance, building a shale play entails several third parties that drill, transport materials, build facilities, and work with system integrators.
Such dependence on various stakeholders brings extra challenges to a business’s operations and digitalisation.
5. Limited Exposure Among Long-Tenured Executives
Energy executives often spend decades within the same company, advancing through energy professionals who remain in their jobs for a long time. Promotion systems remain rigid, promoting conservatism and incrementalism.
On the one hand, this lack of change is beneficial because it mirrors the high-risk and generally complex industry; on the other hand, it means that there is not enough exposure to new ideas that would bring lasting change.
6. Managing Diverse Global Operations
Energy companies are based in many areas of the world. These regions will have different legal systems, labour skills, and proactively varied supply chains and infrastructures.
Managing such discrepancies presents another dimension of dynamism, which does not allow blockage of digital solutions.
If you want to implement AI in your energy company and you want to avoid the hassle, you can proceed according to this scheme developed by McKinsey Research:
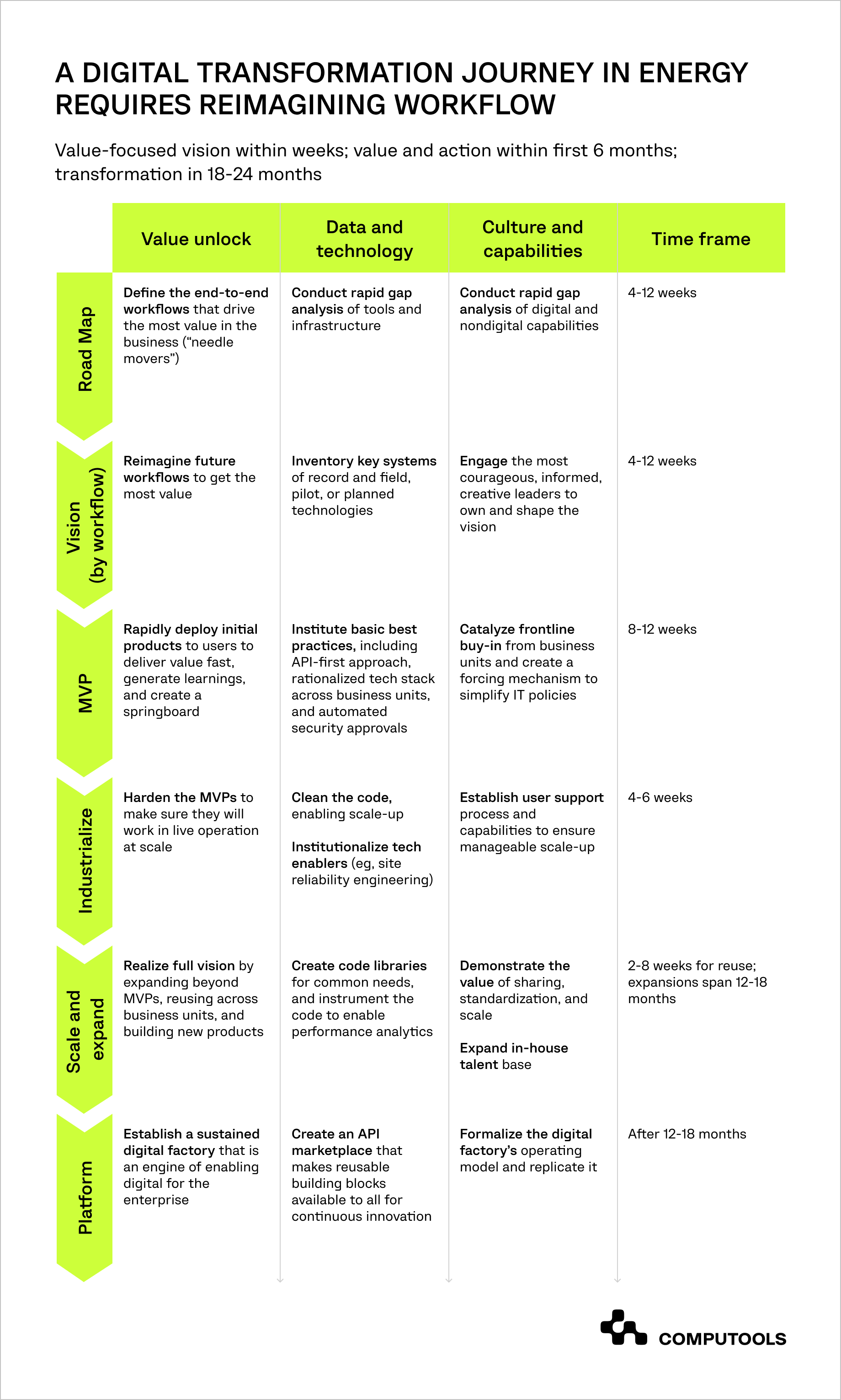
In order not to make a mistake at any stage you can work with a company that will help you study the processes, not only select, but also develop and implement the most optimal solution.
Expertise in the Energy Industry
As an AI development company, we bring unmatched expertise in the energy industry, delivering tailored solutions that address your unique challenges.
From custom AI software to scalable systems, our AI development partner services ensure seamless implementation and value delivery.
We’ve successfully implemented case studies showcasing how AI can transform operations, reduce costs, and promote sustainability in the energy sector. Let us help you harness the potential of AI for your business needs.
Ready to explore AI for your energy business? Contact us today for a consultation at info@computools.com.
Computools
Software Solutions
Computools is an IT consulting and software development company that delivers innovative solutions to help businesses unlock tomorrow.








“Computools was selected through an RFP process. They were shortlisted and selected from between 5 other suppliers. Computools has worked thoroughly and timely to solve all security issues and launch as agreed. Their expertise is impressive.”