Safeguarding your organisation from cyberattacks requires creating a culture that values safety and awareness.
Although many business leaders equip their companies with tools and systems for network protection, they frequently struggle to ensure employees follow business cybersecurity policies and best practices.
This compliance gap makes organisations vulnerable, especially when employees accidentally click on suspicious links or download unauthorised software that may contain malware.
In this article, we will explore why conventional awareness programs are failing to meet expectations and discuss practical steps you can take to promote secure behaviours among employees.
Additionally, we’ll discuss how to find dependable cybersecurity services to help realise your goals more efficiently.
Cybersecurity Incident Statistics
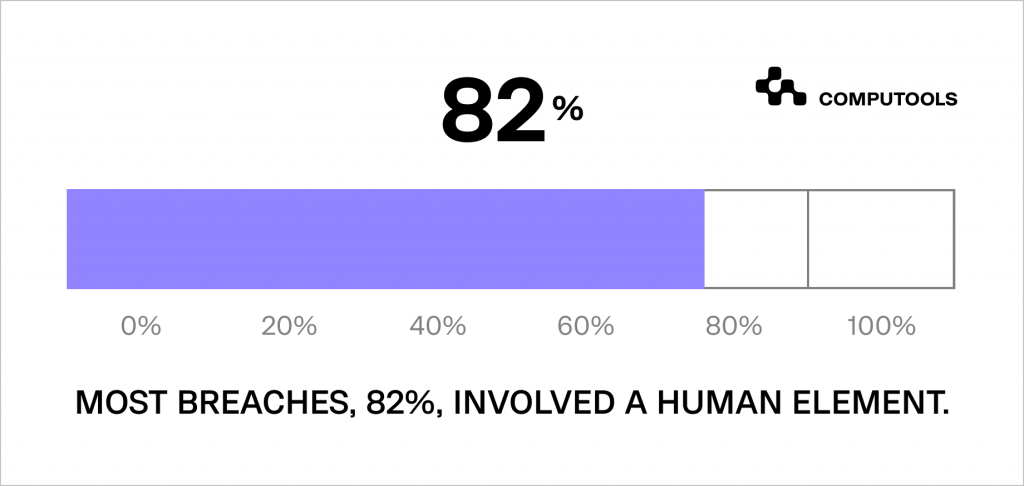
According to the most recent Data Breach Investigations Report, 82% of confirmed data breaches within organisations were due to human factors.
This number suggests that many security problems at work could be prevented with measures that address human mistakes or deliberate internal actions.
CNBC has also highlighted that employee carelessness is the leading reason behind data breaches.
Behaviours contributing to cybersecurity issues include failing to secure devices, opting for simple passwords, and neglecting device updates.
Sure, data breaches caused by human error or system malfunctions typically result in lower costs compared to those caused by hackers. Yet, the impact of employee carelessness shouldn’t be downplayed.
The IBM 2023 Cost of a Data Breach Report, which surveyed over 550 organisations affected by data breaches, revealed that the average cost of breaches caused unintentionally by human errors has reached $US4.45 million, marking a 15% rise in the past three years.
Many might think that negligent behaviour results from a lack of cybersecurity awareness.
However, a recent survey by Gartner showed that employees still engage in risky activities, like opening emails from unknown senders on work devices, knowingly.
So, we can assume that the issue isn’t just about awareness, which is the main emphasis of current Security Awareness Computer-Based Training (SACBT) programs, but rather about human behaviour itself.
Today, businesses are realising that simply increasing employee awareness of security measures is not enough to reduce cybersecurity risks stemming from easily preventable employee mistakes effectively.
Companies that are serious about managing human-related business cybersecurity risks need to take additional steps.
4 Most Common Cybersecurity Mistakes by Company Employees
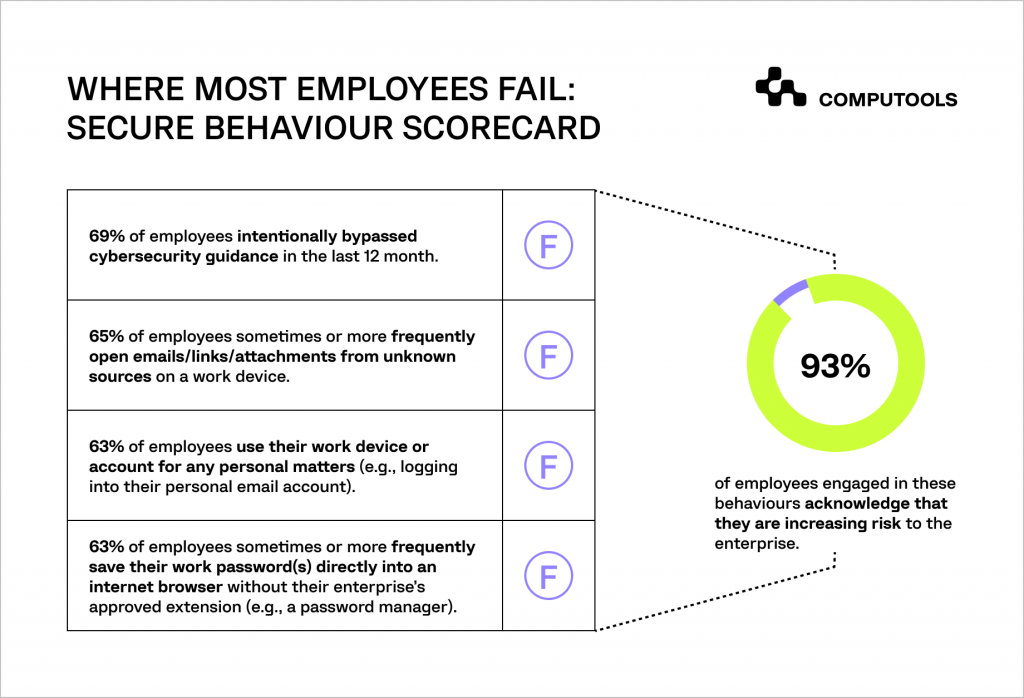
A survey conducted by Gartner among 1310 employees from various companies revealed a list of the most common employee mistakes.
1. Disregard for Security Guidance
A concerning 69% of respondents acknowledged deliberately ignoring company security guidance within the past 12 months.
Such behaviour poses immediate risks to the security of the organisation’s data and systems and reflects a broader issue of employee engagement with security policies.
When employees disregard security guidance, they increase the likelihood of falling victim to cyberattacks such as phishing and data breaches.
Moreover, this trend signals a need for businesses to reassess their approach to security awareness training and communication strategies.
Failure to address this gap can result in severe consequences, including financial losses, reputational damage, and legal liabilities.
2. Susceptibility to Phishing
Phishing continues to pose a significant threat, with 65% of surveyed employees admitting to opening emails, links, or attachments from unfamiliar sources on their work devices.
Phishing scams, where cybercriminals impersonate trusted organisations via emails or texts, have become more sophisticated over time.
They trick victims into downloading harmful software or visiting fake websites. Sometimes, these phishing attempts appear more legitimate by using authentic company logos and email addresses.
The COVID-19 pandemic has also led to a surge in online scams, with fraudsters exploiting people’s trust by pretending to be non-profit organisations or health agencies.
3. Misuse of Work Resources
A notable 63% of employees use their work devices or accounts for personal activities.
This misuse not only diverts resources but also increases the risk of exposing company networks to external threats through non-work-related websites and downloads.
Additionally, mixing personal and work-related activities on the same device or account blurs the lines between personal and professional data, making it challenging for the organisation to maintain data privacy and compliance with regulatory requirements.
This lack of segregation increases the likelihood of cybersecurity incidents, such as data leakage or unauthorised access to sensitive information.
4. Poor Password Practices
Equally concerning is that 63% of employees save their work passwords directly in internet browsers, sidestepping more secure options like password managers.
Weak or predictable passwords can be easily compromised, especially those based on personal information or simple keyboard patterns.
Also, the habits of storing passwords in plain text, publicly displaying them, or relying on insecure password managers expose company data to unnecessary risk.
4 Strategies to Achieve Secure Employee Behaviours
Conventional approaches to delivering curriculum-based programs centred on cybersecurity awareness are no longer effective.
Soon, the main cybersecurity frameworks will emphasise monitoring shifts in behaviour rather than focusing solely on compliance training.
Cybersecurity leaders must adopt strategies that place humans at the core to encourage secure decisions informed by risk comprehension.
1. Redefine Security Initiatives
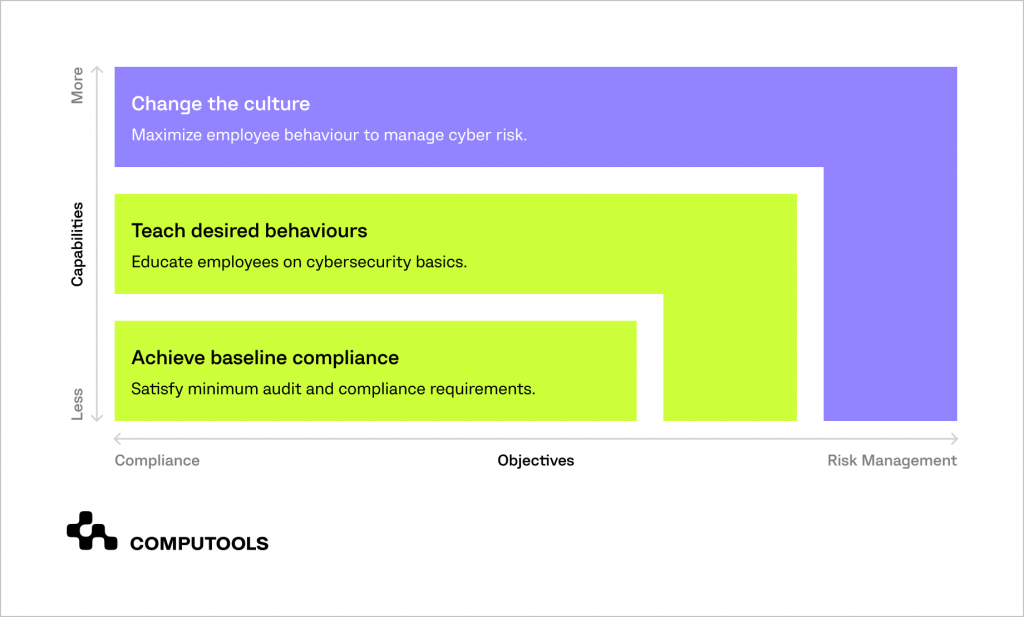
Shift the focus away from merely meeting minimum compliance requirements. Instead, aim to redevelop security awareness initiatives by prioritising and enhancing human behaviour.
Implement strategies and measurements designed to transform the organisational culture regarding security matters.
Steps to take:
• Establish baseline compliance
Incorporate training modules and integrate them with a Learning Management System (LMS) platform to ensure structured and accessible learning.
Then, measure the effectiveness of these training programs by tracking the rates at which employees complete the training.
• Promote the desired secure employee behaviours
Use mock phishing simulations and assess individual human risk scoring to educate and evaluate employee responses to potential threats.
Monitor improvement and awareness by analysing the rates at which employees click on simulated phishing emails.
• Transform organisational security culture
Implement automation and data integration techniques to streamline and enhance the detection and reporting processes.
Evaluate the cultural shift towards proactive security measures by the number of actual attacks detected and reported by users.
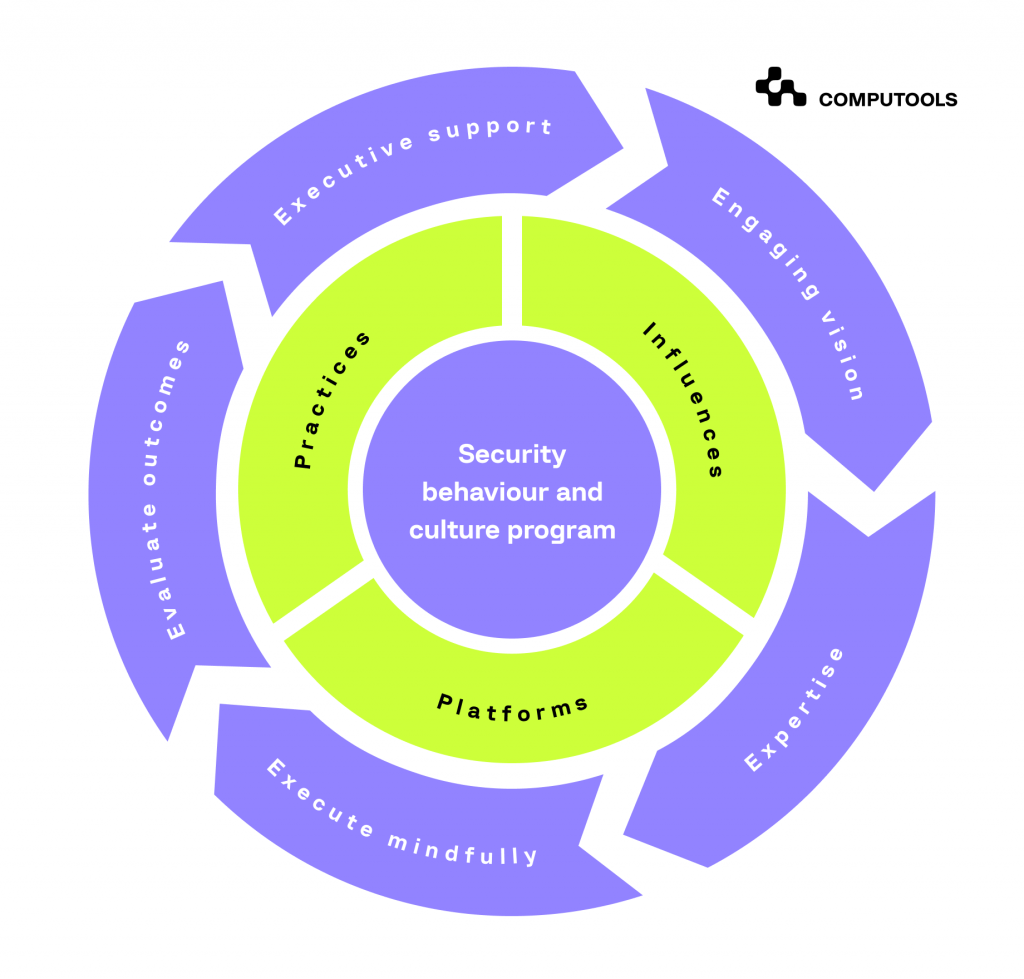
2. Implement the PIPE Framework
Use the PIPE (Practices, Influences, Platforms, and Enablers) Framework to develop and implement a security behaviour program, reducing preventable risks.
The PIPE Framework is designed specifically for Chief Information Security Officers (CISOs) to cultivate a robust security-conscious culture within their organisations.
Steps to take:
• Secure executive buy-in
Gain the support and commitment to cybersecurity of top executives for a shift towards a more security-focused organisational mindset.
• Define success
Clearly envision what success looks like for the program. Ensure the necessary knowledge and resources are available to achieve these goals.
• Track and report
Regularly measure the effectiveness of the program and communicate its benefits to secure continued support.
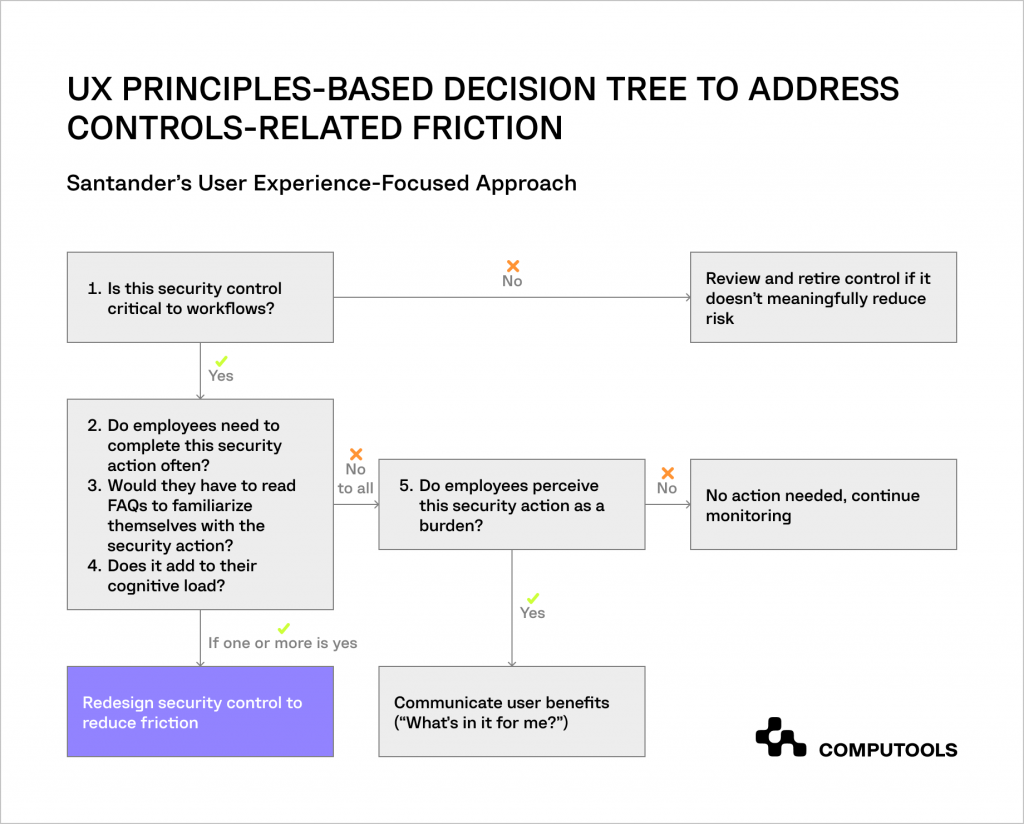
3. Incorporate User Experience into Cybersecurity Measures
To alleviate the burden that cybersecurity preventive measures often impose on employees, you have to move beyond a purely operational view of control management.
Incorporate principles of UX design to adopt a more people-centred approach to cybersecurity and ease the often friction-laden interaction between security protocols and daily work tasks.
Steps to take:
• Identify sources of friction
Implement methods to pinpoint where and how security measures are causing disruptions.
This could involve surveys, feedback sessions, or data analysis to understand their impact on day-to-day operations.
• Assess and remove outdated controls
Regularly review cybersecurity measures to identify any that are outdated or no longer effective to reduce unnecessary workload.
• Foster a UX mindset in cybersecurity teams
Encourage teams to consider the impact on end-users in their designs and evaluations.
• Introduce user-friendly ‘guided bypass’ options
Develop mechanisms that allow for secure, temporary circumvention of certain controls when they obstruct critical work tasks, ensuring these bypasses are monitored and safe.
Adopting this revised approach can result in tangible improvements, including:
– An uptick in the reporting of security incidents and phishing attempts
– A decrease in the use of unauthorised technologies or tools
– A surge in employee interest and participation in cybersecurity training sessions
4. Create Role-Specific Cybersecurity Training Programs
Customise cybersecurity training to include practical exercises that mirror situations employees might actually encounter in their specific job functions.
Steps to take:
• Develop customised scenarios
Craft training scenarios and questions that are directly relevant to the real-life challenges employees might face in their positions.
This method helps in equipping them with the skills and knowledge necessary to navigate security threats.
• Offer multiple solutions
In the real world, security decisions are seldom clear-cut. Design your training to acknowledge multiple correct approaches to a problem, mirroring the complex nature of real-life cybersecurity dilemmas.
• Implement interactive learning paths
Adopt an interactive “choose your own adventure” style for the training program. This design allows the training to adapt dynamically based on the choices employees make, offering a more personalised and engaging learning experience.
Each decision leads to different scenarios, helping employees understand the consequences of their actions in a safe environment and building secure employee behaviours.

Computools
Software Solutions
Computools is an IT consulting and software engineering company that delivers innovative solutions to help businesses unlock tomorrow. Our clients represent a wide range of industries, including retail, logistics, finance, healthcare, and others.
Mini-Guide to Selecting a Cybersecurity Partner for Businesses
Having learned the best cybersecurity principles for your business initiatives, it’s now time to select the appropriate service provider to bolster your efforts carefully.
We’ve outlined two important considerations when partnering with a vendor: criteria for evaluation and steps for choosing the optimal partner.
Criteria for choosing
1. Demonstrated subject matter expertise
Ensure the partner has a robust foundation in cybersecurity practices. Look for evidence of its knowledge and skill set, such as certifications, published research, or a history of solving security challenges similar to yours.
2. Compatibility with the company’s needs and industry requirements
The right partner should have a deep understanding of your industry’s regulatory environment.
This includes familiarity with industry-specific standards and regulations, as well as the ability to tailor its approach to fit your company’s culture and operational needs.
3. Comprehensive cybersecurity services
Choose a partner that offers a variety of cybersecurity services and solutions.
From risk assessment and incident response to ongoing monitoring and training, a huge suite of services ensures that all aspects of your cybersecurity needs are covered.
4. Strong commitment to customer support
Effective support is a must in the cybersecurity realm. Clear, responsive communication and a willingness to offer assistance when needed, including helping you comprehend complex security issues and collaborating closely to devise and implement effective cybersecurity strategies, are highly significant.
Evaluating potential partners
1. Assess credentials and certifications
Begin by verifying the cybersecurity partner’s qualifications and certifications. These credentials are critical as they demonstrate the partner’s commitment to its field and its expertise and reliability.
Look for industry-recognised certifications such as CISSP, CISM, or ISO 27001.
2. Evaluate client testimonials
Investigate the partner’s case studies and the feedback it has received from previous clients to understand its experience. Positive testimonials provide insights into the partner’s customer satisfaction levels as well.
3. Check for ongoing support and incident response capabilities
Assess the partner’s responsiveness to the incidents and its cybersecurity reactive measures.
A partner that offers robust incident response services and is ready to support you around the clock can reduce the impact of any breaches that may occur.
4. Review compatibility with your technology stack
Ensure the cybersecurity partner can work efficiently with your organisation’s technology stack.
Compatibility with your existing systems and processes is necessary for seamless integration of security measures and minimising disruptions to your operations.
Conclusion
Employee mistakes or oversights pose significant cybersecurity risks, potentially creating vulnerabilities and leading to data breaches within an organisation. Such errors include using weak passwords and sharing sensitive information, as well as neglecting software and device updates.
Although these actions might appear minor, businesses must invest in training programs to educate employees on cybersecurity best practices and the critical importance of following security policies. The financial or reputational damage resulting from these errors can be catastrophic.
Furthermore, incorporating cybersecurity services into your strategy can offer substantial benefits by providing tailored solutions to address particular vulnerabilities and defend against evolving threats.
Want to get expert cybersecurity assistance? Drop us an email at info@computools.com to schedule a consultation with our subject matter specialists.








“Computools was selected through an RFP process. They were shortlisted and selected from between 5 other suppliers. Computools has worked thoroughly and timely to solve all security issues and launch as agreed. Their expertise is impressive.”