Digital threats pose a significant risk to businesses of all sizes, from large enterprises to smaller online stores. Given the complexity of website defence, especially in the face of constantly evolving business cybersecurity trends, website owners need to be both aware and prepared.
Most Common Business Website Security Threats
With cybersecurity threats evolving not just daily but hourly, businesses – particularly smaller ones – are increasingly at risk of sophisticated attacks. Cybersecurity Ventures projects a worrying scenario, estimating that the global cost of cybercrime could reach US$10.5 trillion by 2025.
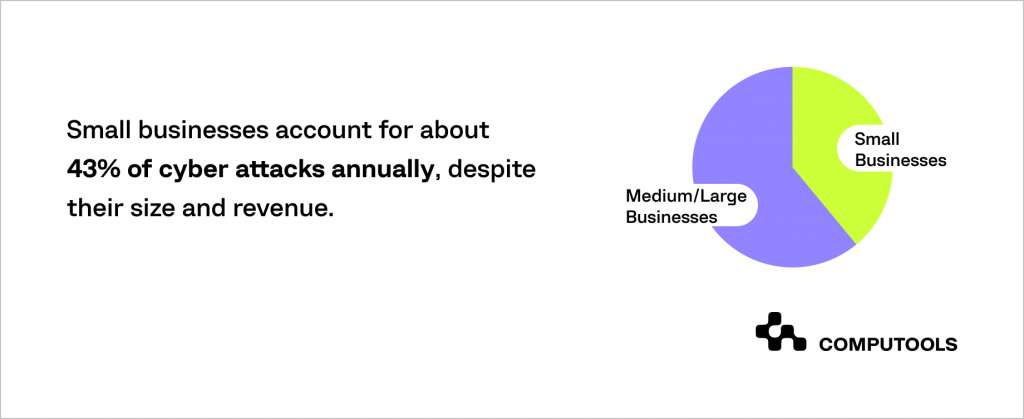
Accenture’s cybercrime study emphasises this challenge, revealing that 43% of cyberattacks specifically target small businesses. What’s concerning is that only 14% of them feel adequately prepared to defend themselves.
The fallout from cyberattacks extends beyond disrupting day-to-day operations; it can lead to significant damage to crucial IT assets and infrastructure. Often, companies, particularly those with limited resources, find it challenging to recover from these breaches.
As a business leader, it’s necessary to grasp the specific targets and consequences of digital threads. This understanding allows you to minimise potential damage, maximise the effectiveness of your cybersecurity efforts and proactively work to prevent future incidents.
Before we delve into practical tips on how to protect business websites, let’s explore some common web security challenges that could pose a risk to your online presence.
1. Data breaches
The business world today faces significant risks from data breaches, arising from either accidental exposure or deliberate cybertheft. As reported by Statista, during just the first quarter of 2023, over six million data records were exposed due to these breaches.
Cybercriminals actively exploit websites and web application vulnerabilities to access sensitive information for financial gain or to infiltrate company networks.
Common targets include financial and medical data, but breaches can also expose student records, photos or customer private details.
The consequences of data breaches, except for financial loss, can lead to fines and a severe impact on business reputation and public trust.
2. A distributed denial-of-service attack (DDoS)
A substantial threat to business website security, DDoS attacks disrupt services by overwhelming servers with excessive internet traffic, rendering websites inaccessible.
The aim of DDoS attacks is to create an overload. When the system or any other resource is incapacitated, the owner faces the loss of operational capability and reputational damage. These attacks can be motivated by various reasons, including financial gain.
As indicated by Gitnux, the expenses associated with DDoS attacks are on the rise, and SMBs are now allocating an average of US$120,000 per attack. This trend is likely attributed to the increasing adoption of cloud systems.
The impact of DDoS attacks is significant, causing service disruptions, especially when combined with other threats.
3. Attacks targeting cloud systems
The increasing reliance on cloud infrastructure for hybrid work has introduced new security challenges. Attacks targeting cloud systems exploit vulnerabilities in cloud models, leading to various risks due to insecure configurations and mismanaged permissions.
Weaknesses in securing API endpoints within cloud environments can allow attackers to inject malicious code or manipulate data requests.
Attackers may also exploit misconfigurations in a multi-tenant cloud environment, jeopardising the security of multiple websites sharing the same infrastructure. Such attacks can lead to widespread data breaches or service disruptions, affecting multiple aspects of web security.
4. Cross-site request forgery (CSRF)
CSRF attacks pose a significant threat to websites, particularly those handling sensitive user actions like financial transactions. CSRF attacks trick a user into performing actions using their own credentials without their knowledge.
For example, a hacker creates a form with his bank details hidden in it and sends it to users of a financial website.
The form, disguised as a ‘get rich quick’ link, triggers an HTTP POST request when clicked. This request includes the user’s cookies, which the server uses to verify the user’s identity and authorise transactions.
As a result, any logged-in user who clicks the link unknowingly sends money to the hacker, enabling him to profit from their unawareness.
5. Cross-site scripting (XSS)
Imagine browsers manipulated to execute malicious scripts upon receipt, leading to potential data theft, malware installation or redirection to deceptive sites. This is cross-site scripting (XSS) attacks in action.
Guarding against these cybersecurity threats involves meticulous handling of data inputs and denying special characters or symbols to thwart code injection attempts.
Left unchecked, XSS attacks can lead to severe consequences, including session hijacking, form manipulation and server-side request forgery attacks.
6. SQL and code injections
While structured query language (SQL) is a powerful tool for database queries, it becomes a threat when attackers exploit vulnerabilities in application code. Through SQL injection, cybercriminals insert malicious queries into standard online form fields, like login boxes on websites.
As per Security Escape, 42% of hacker efforts directed at public-facing systems involve SQL injection. This technique has proven successful in widely used codebases, including popular platforms like WordPress plugins.
A single vulnerability in the code can compromise numerous websites, granting attackers access to sensitive corporate data like customer files and financial information.
7. Broken authentication
Digital security heavily relies on the strength of passwords. Passwords are vulnerable as they can be easily cracked by automated software attempting various combinations.
Adding to this risk, web developers sometimes unintentionally compromise website protection by using default passwords linked to their web administrator accounts. According to the 2023 Verizon Data Breach Investigations Report, a significant 74% of data breaches occur due to human elements.
If a hacker gets hold of a website’s username and password, they can carry out a range of malicious activities, from defacing the webpage to making files irretrievable.

Computools
Software Solutions
Computools is an IT consulting and software engineering company that delivers innovative solutions to help businesses unlock tomorrow. Our clients represent a wide range of industries, including retail, logistics, finance, healthcare, and others.
7 Steps to Ensure the Security of Your Website
Companies lacking effective business website cybersecurity measures are at risk of being targeted by malware and cybercriminals, leaving their IT infrastructure, web applications and networks exposed to potential unethical activities.
We’ll explore seven methods to enhance your website’s security, ensuring you have a robust plan to prevent unforeseen incidents.
1. Timely software and security maintenance
Regularly updating your website’s software, including your content management system (CMS) like WordPress, is critical for maintaining web page security. These updates often address vulnerabilities that, if left unpatched, could be exploited by cybercriminals.
To prevent such exploitation, you have to consistently monitor for and promptly install these updates, particularly in your WordPress admin panel. This vigilant approach to software maintenance helps seal potential security gaps and safeguard your site.
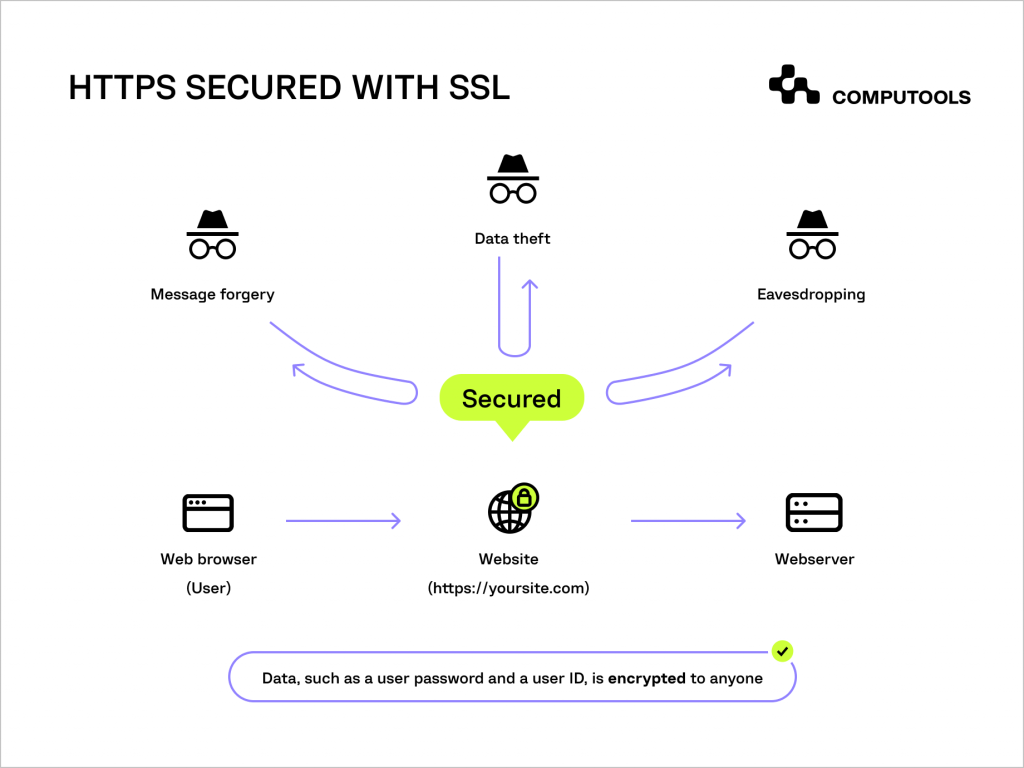
2. Mandatory SSL encryption
Beyond software updates, implementing Secure Sockets Layer (SSL) encryption is fundamental for data security and protecting information transmitted between your web server or firewall and users’ web browsers.
By installing an SSL certificate, you ensure that this data is encrypted, reducing the risk of interception during transit. To further enhance credibility and security, consider advanced SSL options like organisational SSL or extended validation SSL, which display your organisation’s details.
However, keep in mind that while SSL encryption secures data in transit, it does not protect the website itself from other forms of attacks.
3. Website firewall
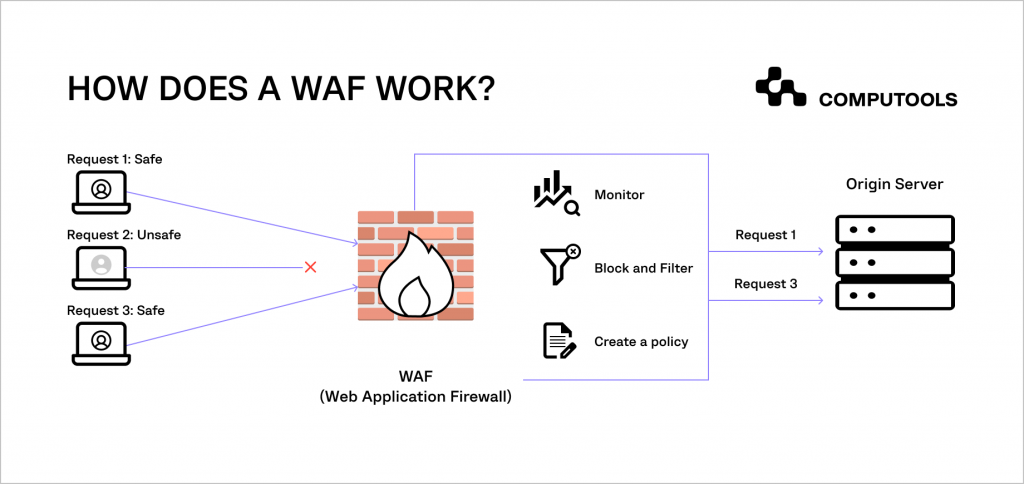
However effective, SSL certificates alone are not enough to fully protect your website. Vulnerabilities in your web application can lead to various risks, such as data interception, malicious redirections, ransomware attacks or data loss.
A web application firewall (WAF) is a specialised defence mechanism designed to counter these threats. By integrating a WAF, you not only add an extra layer of business website security but also can focus more on your professional activities, knowing your online presence is guarded against a wide range of digital threats.
4. PCI DSS compliance
For websites that handle credit card payments, adherence to the payment card industry data security standard (PCI DSS) is the number 1 rule. This standard is designed to secure online transactions and minimise the risk of data theft during financial exchanges.
To become PCI compliant, you need a concerted team effort along with strict adherence to a set of website security policies.
This includes implementing security measures such as maintaining up-to-date firewall configurations, regularly updating anti-virus software and routinely changing passwords.
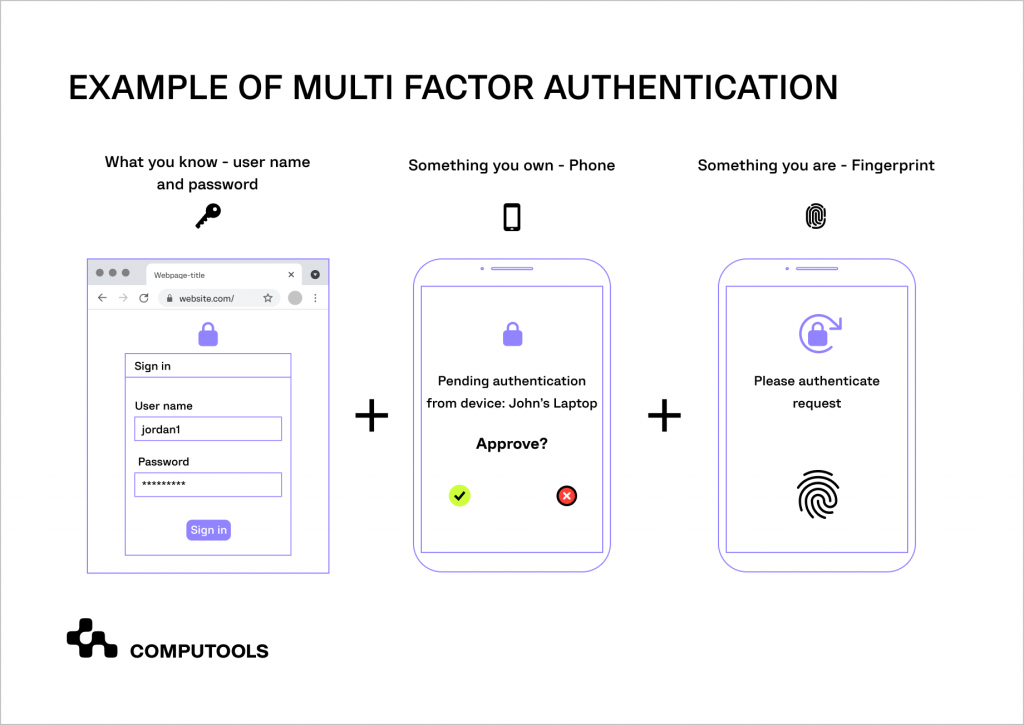
5. Multi-factor authentication (MFA)
Implementing multi-factor authentication (MFA) is a powerful step in enhancing your business website security.
MFA adds an extra verification layer beyond passwords, such as a one-time password, QR code, or push notification on a mobile device, significantly strengthening defences against unauthorised access.
Coupling MFA with SSL data encryption can deter hackers, even if they manage to obtain one set of credentials.
For website owners, especially those running small and medium-sized businesses, prioritising this basic security tool is necessary for building trust and a robust company reputation.
6. Strengthening cybersecurity through employee education
Securing a website, whether it’s built on WordPress or is a static HTML site, involves more than just installing security plugins. It requires fostering a culture of awareness and understanding of website security best practices among employees.
Cybersecurity training for your team should cover critical topics like GDPR compliance and password security.
Whether through workshops or classes, educating your staff on business website cybersecurity is a significant step towards enhancing your overall security posture. A well-informed team is a key asset in maintaining a secure and safe online presence.
7. Automated website back-ups
To maintain smooth customer engagement, businesses have to quickly recover from cyberattacks or issues during website updates.
Use an automated site back-up tool that rapidly restores the latest, unaffected version of your website if any unexpected problems occur.
Choose a service that conducts daily website security checks and back-ups to avoid reverting to an outdated version in case of a system crash.
The main goal of this approach is to minimise downtime and ensure a continuous online presence, preserving your vital connection with customers.
Responding to a Cyberattack on Your Business Website
If your efforts to defend against cyberattacks haven’t been enough to ensure robust security for the website, it’s time to consider recovery steps.
Recovering from a cyberattack requires both immediate actions and a long-term strategy to prevent future incidents.
1. Immediate Response Steps
• Containment
As soon as you detect a cyberattack, your first step should be to contain the breach. This may involve taking the website offline temporarily to prevent further damage.
• Assessment
Assess the scope and impact of the attack. Determine which data and systems are affected and the type of attack you’re dealing with.
• Notification
Notify relevant stakeholders, including your customers, employees and partners, especially if sensitive data has been compromised. Transparency is key.
• Legal compliance
Check your legal obligations. In many regions, businesses are required to report cyberattacks to regulatory authorities, especially if personal data is involved.
2. Long-Term Response and Prevention
• Partnering with a reliable Software Engineering company
Select a web development company that aligns with international standards and legal obligations.
Look for an ISO/IEC 27001:2022 certification, a standard for security management and ensure compliance with data protection laws such as GDPR and relevant industry certifications.
Computools, for example, holds ISO/IEC 27001:2022 and ISO 9001:2015 certifications, showcasing our commitment to high-quality standards in security and management systems.
These certifications also reflect our dedication to responsible practices in line with international standards.
• Collaborative security planning
Collaborate with your web development services provider to craft a comprehensive security plan. This plan should encompass both the development and maintenance phases of your website, ensuring continuous monitoring, support and updates.
Also, your vendor should possess the necessary field expertise to ensure the plan considers all the intricacies of your industry.
Computools leverages its subject matter expertise to ensure software solutions meet all legal and security requirements. This approach minimises the risks, allowing us to provide robust solutions for our clients.
Conclusion
Remember that ensuring business website cybersecurity is an ongoing effort, not a one-time fix. Instead of a set-it-and-forget-it approach, consider it as a continual process that demands consistent evaluation to minimise overall risk.
Adopting a systematic method for website protection involves multiple layers of defence converging to create a unified shield.
If you want to discover the latest trends in business website cybersecurity, reach out to us via email at info@computools.com.








“Computools was selected through an RFP process. They were shortlisted and selected from between 5 other suppliers. Computools has worked thoroughly and timely to solve all security issues and launch as agreed. Their expertise is impressive.”