In the world of payments, there are different messaging standards designed to facilitate the exchange of information related to financial transactions. The International Organization for Standardization (ISO) developed these regulations to make global business communication simpler and more secure.
The SWIFT network that traditionally facilitated payments is giving way to the next-generation ISO 20022 standard for financial messaging. This new implementation is expected to be the singular, global rule governing high-value payment systems for all reserve currencies.
In 2022, Statista conducted a survey revealing varied approaches to the new ISO regulation within different bank departments. Notably, 20% of strategy-focused senior executives saw the move as necessary but lacking short-term benefits.
Additionally, Forbes reported that only 8% of European banks were confident in the industry’s readiness for such a shift.
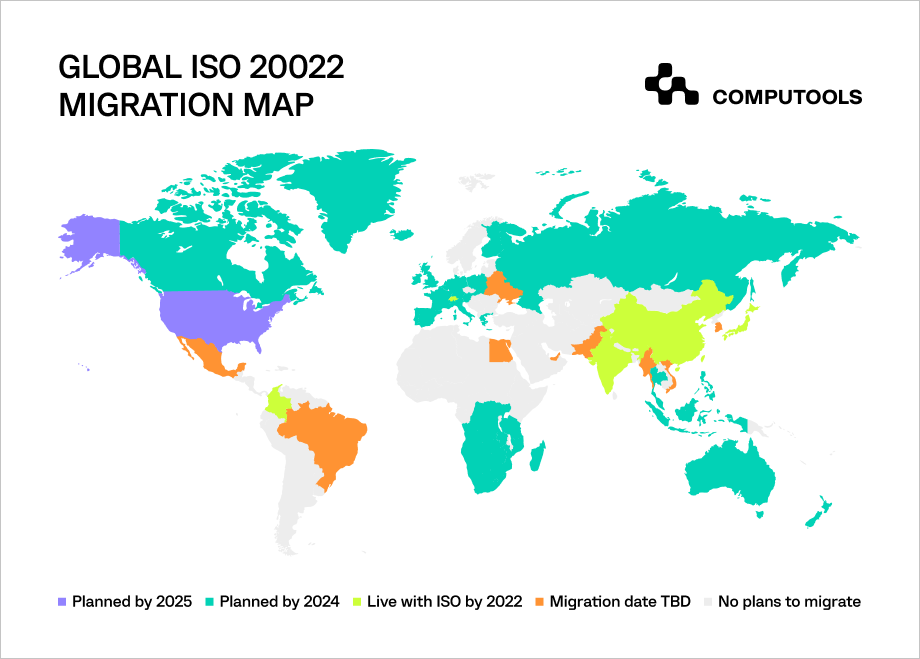
The transition to the new system began in March 2023, necessitating complete standard integration by banks before November 2025.
With some time elapsed, we can now assess whether the concerns of banks and corporations were justified and observe how the adoption of the new system has already influenced and continues to impact the financial industry.
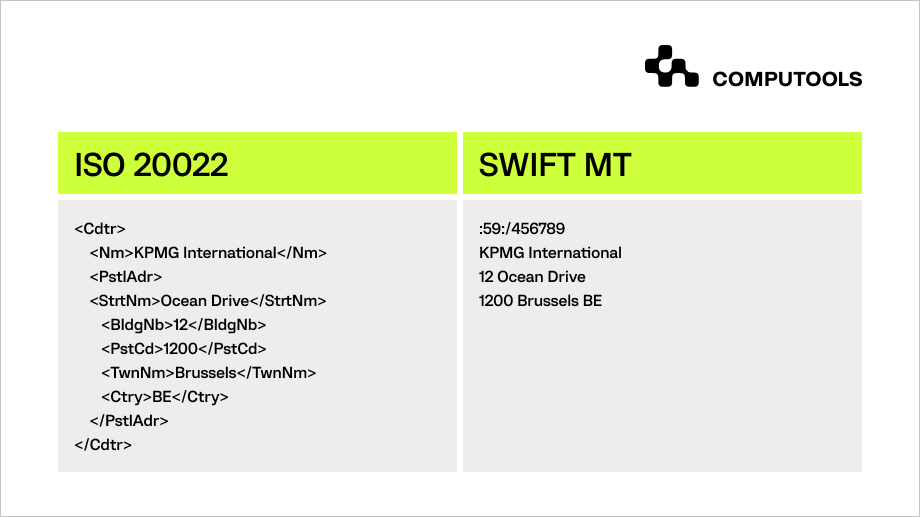
In contrast to SWIFT, ISO 20022 introduces a more comprehensive and standardised messaging format, providing a broader scope that extends beyond traditional payment systems.
When is the deadline for the migration process?
The coexistence phase for 20022 and MT messaging standards started on 20 March 2023. This period, where both standards are accepted, will end in November 2025, when MT messages will no longer be used.
Banks can adopt the new format at their own speed between 2023 and 2025. Plans for adoption are still developing in every market, and additional clarity will be offered gradually.
Why adopt a new standard?
Traditionally, major banks and financial institutions have independently devised and enforced their own communication standards, often without collaboration.
The introduction of an international messaging standard offers a solution to streamline communication and global financial services between domestic and international agencies. This is achieved by incorporating diverse syntax and semantics into a shared codex.
Implemented through a standardised modelling methodology and protocols like Extensible Markup Language (XML) and Abstract Syntax Notation (ASN.1), the system provides translated syntax and semantics for non-Latin alphabets.
It effectively bridges communication gaps in the international finance landscape and facilitates the establishment and management of partner relationships.
Impact of the Standard on the Financial Sector
1. On the Financial Industry and Payment Systems
The global move to the new standard by major payment systems is one of the most significant changes ever in the financial services industry.
In over 50 countries, the new standard will soon replace existing domestic systems and payment standards, making cross-border payments more consistent across banks, financial institutions and other systems.
The standard allows for more detailed data, which will eventually reduce the need for manual intervention, making bank transactions smoother for everyone involved. This improvement in readability makes it easier for different financial institutions and settlement networks to work together across regions.
2. On Financial Institutions
The shift to a new standard impacts various banking processes, including know-your-customer checks, electronic banking, liquidity management and reporting. The success of each bank depends on its strategy and openness to change, despite the time and financial investment required for the migration.
While the transition demands significant resources, it unlocks a new level of efficiency and cost-effectiveness. Given the diverse approaches in different countries, banks must closely monitor adoption timelines and adapt accordingly. Not all financial institutions were ready to adopt the standard immediately.
Budget constraints may lead some banks to convert existing SWIFT MT messages to ISO 20022 without altering their core systems. However, this quick fix lacks long-term technical efficiency gains.
The greater the integration of the messaging standard with the core banking systems, the less likely the bank is to experience service downturns in the long term.
Those opting not to migrate may find themselves unable to provide global financial services as innovative competitors and may need help in collaborating with most businesses.
3. On Fintech Solutions
The standard acts as a common framework for new fintech solutions like distributed ledger technology, smart contracts and APIs. Recognised as the standard language for financial industry initiatives, it supports the smooth integration of these technologies.
ISO 20022 compliance ensures the straightforward implementation of FinTech solutions, making the most of their complementary roles within the industry.
With the standard’s global acceptance, fintechs can create applications tailored to diverse payment ecosystems, like accommodating European IBAN requirements and Canadian clearing codes.
This integration makes cross-border payments smoother by reducing the likelihood of rejections and ensuring that legitimate transactions are less likely to be scrutinised. The new regulation stands out as a vital facilitator, empowering fintech innovation in the global financial landscape.

Computools
Software Solutions
Computools is an IT consulting and software engineering company that delivers innovative solutions to help businesses unlock tomorrow. Our clients represent a wide range of industries, including retail, logistics, finance, healthcare, and others.
What Are the Benefits of the Standard for Global Financial Services?
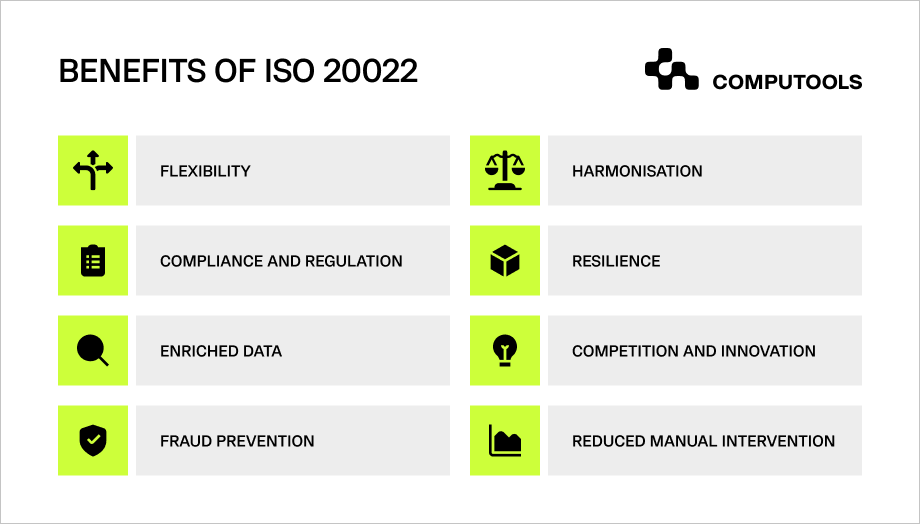
The new regulation brings numerous advantages to the institutions and individuals in the global financial sector.
One of its key benefits lies in its high flexibility compared to SWIFT, enabling extensive customisation.
Moreover, being built on XML, a widely adopted open standard, it encourages competition and facilitates increased interoperability among diverse systems. Some other benefits include the following.
1. Improved Fraud Prevention
Improved fraud prevention measures safeguard the financial system from malicious activities, instilling greater confidence among consumers and fostering trust in the banking sector.
2. Enhanced Precision
ISO 20022 brings detailed information to payments, helping identify transactions, senders, beneficiaries and transfer purposes. It operates within a structured framework, prioritising precision over unrestricted flexibility.
This structured approach enables banks and institutions to customise their operations effectively, ensuring compliance with standardised protocols and allowing them to respond adeptly to changing market demands.
3. Promotion of Competition
Built on the widely used XML standard, the new ISO rules encourage banks to compete by promoting efficiency and interoperability.
The standard establishes a common language for financial messages, enabling banks to offer corporate customers the latest payment options and services, fostering a competitive environment as banks strive to enhance operational efficiency and provide advanced services.
4. Harmonisation
With everyone using the same language, it’s easier for banks worldwide to communicate. This makes cross-border transactions smoother and more efficient. Standardised communication also reduces the likelihood of errors and misinterpretations, improving the overall reliability of financial transactions.
5. Richer Transaction Data
The new regulation allows for more detailed and organised information in payment messages. Richer transaction data enables financial institutions to gain deeper insights into customer behaviour, facilitating more personalised and targeted financial services.
6. Reduced Manual Intervention
The new standard significantly cuts down on manual work, especially for roles like data entry operators and customer service representatives. Automated processes reduce the need for hands-on effort, lightening the workload for these roles.
For instance, data entry operators spend less time fixing errors in financial messages and customer service representatives deal with fewer problems in handling payments. This overall reduction improves operational efficiency and lowers the risk of errors in these important areas.
7. Accurate Compliance Processes
Using the new rules helps banks stick to the regulations more accurately. Accurate compliance processes are crucial for maintaining the integrity of financial operations and ensuring adherence to requirements.
8. Higher Resilience
The new standard significantly strengthens the reliability and resilience of financial operations. It introduces enhanced security measures, including standardised encryption and authentication protocols, to ensure that sensitive financial information is not only transmitted securely but also stored with an increased level of protection.
This robust resilience ensures the seamless continuity of financial services, offering a high level of protection against unforeseen disruptions and cybersecurity threats.
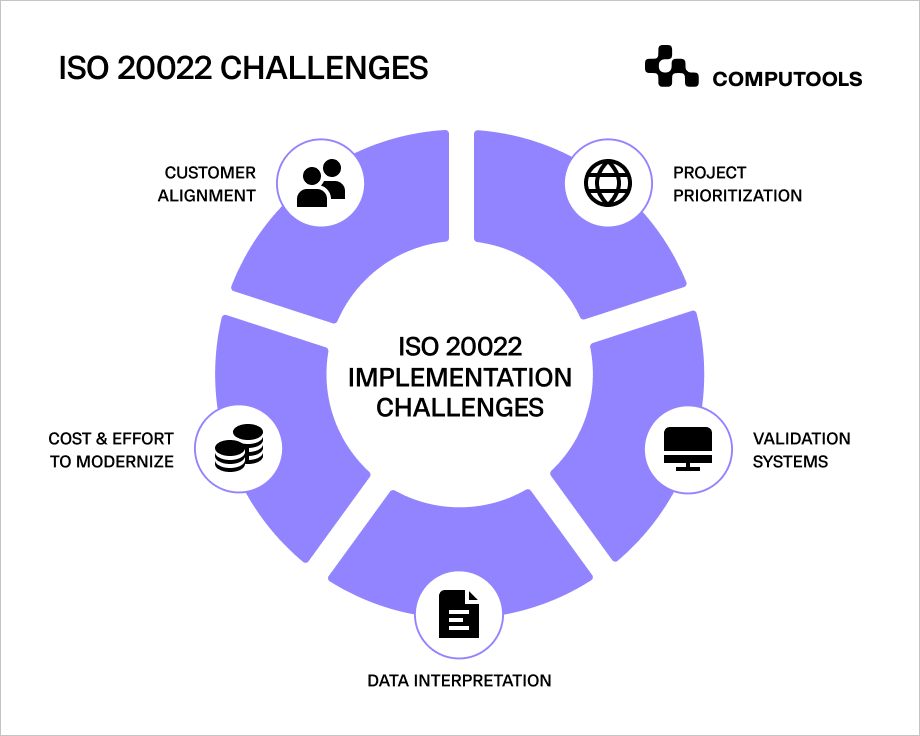
What Are the Implementation Challenges?
Considering the extensive nature of the transformation, encountering significant challenges is inevitable. Here is our perspective on how to minimise their impact and be well prepared.
1. Consistent Data Interpretation
Achieving alignment with partner financial institutions is crucial for a shared and consistent interpretation of the standard, especially across jurisdictions.
This alignment ensures data standardisation across the financial industry, and various payment systems, defining an approach to data governance, quality, harmonisation, migration and ownership.
Related Experience
Computools' Product: Scaler
Systemize and scale your business with our intuitive, secure Scaler Cloud Platform - all by yourself, guided by your own business intuition and our proven methodology
2. Project Prioritisation
Handling the implementation alongside multiple internal projects can pose challenges. Allocating both human capital and financial resources to projects is a pre-planned process, often scheduled months or even years in advance. Hence, securing appropriate resources and budget allocation specifically for the shift becomes crucial.
3. Customer Alignment
Transaction processing involves a reciprocal relationship: banks handle corporate payments forwarded by their customers, requiring them to embrace ISO 20022.
Corporations will seek guidance from their banks during the transition to ensure that comprehensive benefits are realised throughout the entire value chain.
4. Validation
ISO messages are more complex and longer than regular payment messages. Accuracy with data is crucial as each character undergoes validation at various points.
Effective validation requires a strong understanding of the data’s structure and meaning. Missing even a single character can cause delays or rejections in funds transfers.
5. Cost
Banks must make substantial investments in the global migration to the new standard. Determining the priority of jurisdictions, products and services for migration creates competition for funds and resources.
Given the long-term return on investment (ROI) due to migration complexities, banks need to strategically evaluate the business case to communicate benefits effectively to programme sponsors.
How Is Adoption Going?
The ISO 20022 ecosystem has been gradually rolling out over the past few years; however, progress has been relatively slow.
Globally, high-value payment systems, including those in Japan, Switzerland and China, have already transitioned to the new regulation, and other countries are also gearing up to adopt this new standard in the coming years.
While ISO 20022 is acknowledged as the common international standard for financial messaging, the implementation timeline remains uncertain.
As the world undergoes post-pandemic recovery, accompanied by other global crises, and migration efforts persist, financial institutions must dedicate ongoing time and resources to gaining the knowledge and expertise required for a successful transition.
Until the full migration deadline in November 2025, financial institutions, at the very least, must be prepared to receive ISO 20022 payments for cross-border payments and reporting.
Final Words
Realising the advantages of ISO 20022 requires substantial effort. The standard’s influence goes beyond core payment systems, impacting various aspects such as booking systems, embargo and customer verification systems, digital banking, managing available funds, and record-keeping.
The shift isn’t solely about managing cash. Securities, trade finance, global markets and treasury departments must also adeptly process and apply the contained information.
As the deadlines approach, it’s crucial to acknowledge that work still lies ahead.
Discover more about how the fintech industry is navigating the transition to the ISO 20022 standard by reaching out to us via email at info@computuls.com.









“Computools was selected through an RFP process. They were shortlisted and selected from between 5 other suppliers. Computools has worked thoroughly and timely to solve all security issues and launch as agreed. Their expertise is impressive.”