The Growing Importance of Computer Vision in Agriculture
Agriculture is a massive, labour-intensive, and extremely challenging business to operate. Farmers battle labour shortages, rising costs, and the need to practice sustainably. As it continues to grow in importance, computer vision in agriculture is also worth a look at.
McKinsey insights point to this technology’s potential to transform agricultural efficiency.
Since the last 50 years, the agriculture industry has changed enormously. The enrichment of machinery has increased farm equipment’s scale, speed, and productivity to cultivate more land more efficiently. Technology also stimulates global GDP industry value.
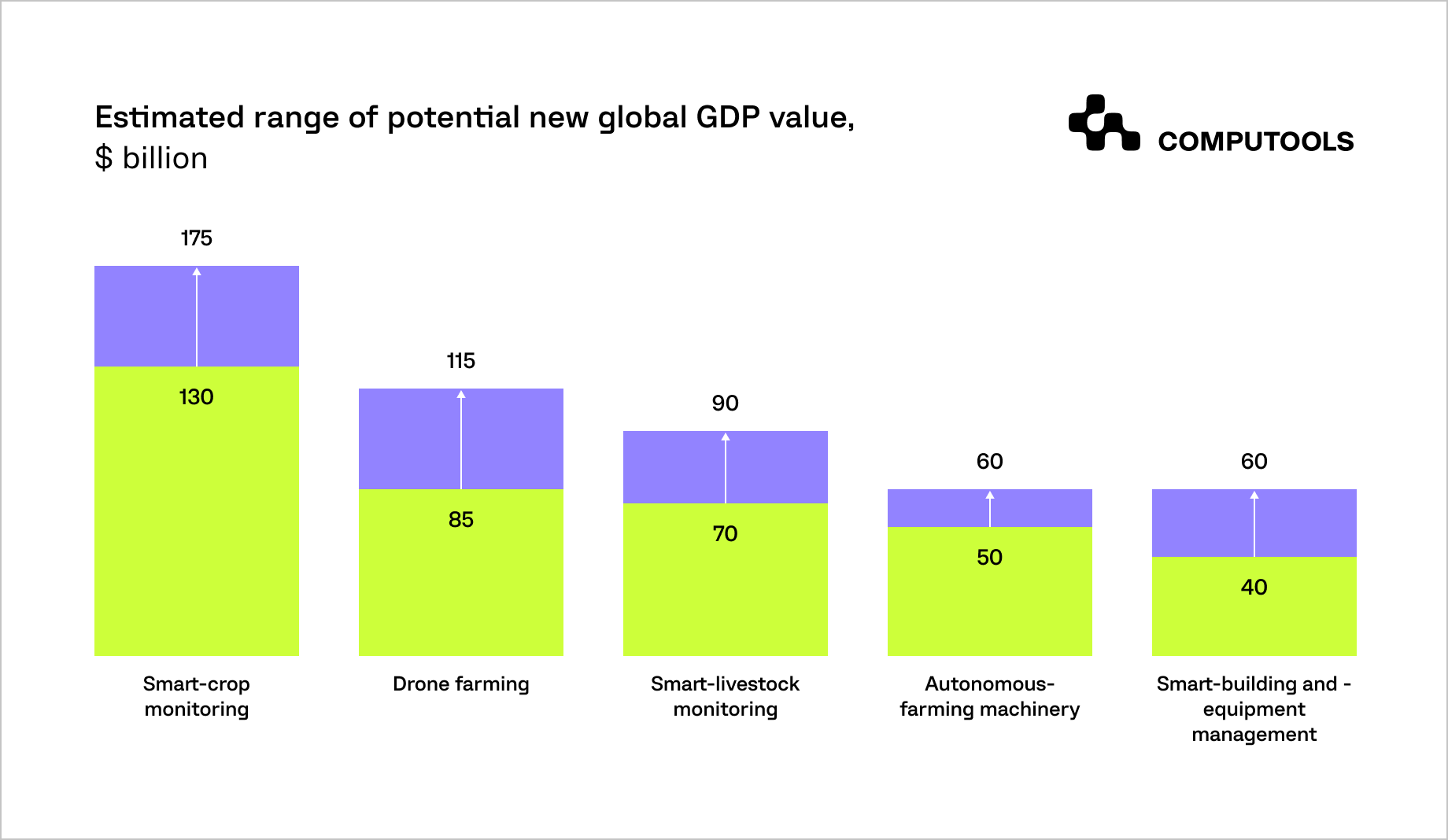
The seed, irrigation, and fertilisers have become vastly improved, and the farmers have increased their yields. Agriculture is in the early days of yet another revolution, built on data and connectivity, at its very heart.
Further increases in yields could be fostered by emerging technologies such as computer vision, artificial intelligence, analytics, connected sensors, etc., which could enhance water and other inputs efficiency and enhance sustainability and resilience in crop cultivation and animal husbandry, respectively.
Over the past few years, many farmers have started consulting data about essential variables such as soil, crops, livestock, and weather.
Yet very few, if any, have had access to the sort of advanced digital tool that could help make these data useful, actionable insights. Less developed regions feature almost complete manual farm work constrained by neither advanced computer vision nor much in the way of equipment.
Exploring the Drivers of Computer Vision in Agriculture
The implementation of computer vision in agriculture is transforming the sector, driven by several key factors.
First, the computer vision benefits, such as enhanced productivity, precise resource use, and better decision-making are widely recognised.
Second, the technology addresses critical challenges, like pest control, crop monitoring, and yield optimisation.
Finally, by integrating computer vision into farming operations, agricultural enterprises can unlock significant opportunities for business growth through smarter, more sustainable practices.
Organisations investing in computer vision development leverage its potential to revolutionise workflows across the agricultural sector.
Key applications include:
• disease detection using real-time imaging,
• irrigation management to reduce water waste,
• predictive analytics for harvest planning.
These applications boost efficiency and accuracy when paired with agriculture software solutions, delivering measurable value. Companies that embrace this technology position themselves as leaders in innovation and sustainability.
Advancements in supporting technologies further accelerate the adoption of computer vision. Providers of agriculture software solutions offer tools like intelligent sensors, data visualisation platforms, and automation systems.
These solutions enable:
• continuous monitoring of field conditions,
• optimisation of machinery performance,
• reduced environmental impact through precise interventions.
By utilising these innovations, agricultural businesses can achieve sustained business growth, ensuring a competitive edge in a rapidly evolving market.
How Computer Vision Helps the Industry: Use Cases
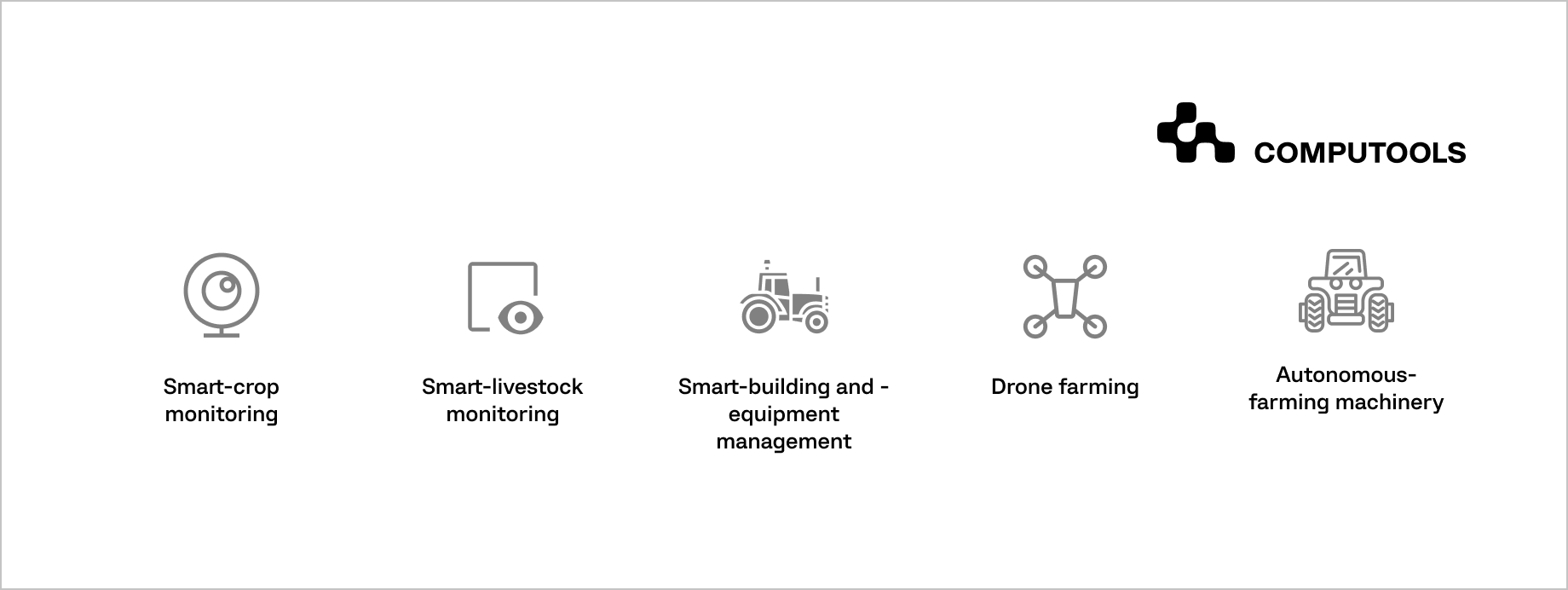
Use Case 1: Crop Monitoring
Computer vision improves crop observation and care. By integrating systems like weather tracking, irrigation, and nutrient management farmers can use resources more efficiently and boost yields.
For example, soil sensors can send images from remote areas of fields, helping farmers make timely decisions and detect early signs of diseases or pests. Smart monitoring can even optimise harvesting by analysing crop quality, such as sugar content or fruit colour.
Use Case 2: Livestock Monitoring
Managing large-scale livestock operations requires early detection of illnesses and better animal care. Sensors and chips can measure vital signs like temperature and pulse, identifying health issues before they spread.
Additionally, environmental sensors can adjust barn conditions, improving animal well-being and meeting consumer demands.
Use Case 3: Building and Equipment Management
Computer vision also supports efficient management of farm infrastructure. Sensors in silos and warehouses can automate reordering, reduce inventory costs, and extend the shelf life of stored goods.
Tools like predictive maintenance systems use computer vision in agriculture to monitor equipment, reduce repair costs, and extend machinery life.
Use Case 4: Farming by Drone
Drones are revolutionising agriculture by quickly surveying crops and herds over large areas. They can analyse fields using computer vision benefits and apply fertilisers or pesticides precisely where needed. Some drones can even plant seeds in hard-to-reach areas, reducing equipment and labour costs.
Use Case 5: Autonomous Farming Machinery
With agricultural and farm machinery software enhanced by precise GPS, sensors, and computer vision, autonomous machines can perform tasks without human intervention.
These smart systems are more efficient, saving fuel and increasing yields.
Additional Benefits of Computer Vision
Computer vision solutions provide indirect benefits to the agricultural business, such as freeing up farmers’ time.
In regions with fragmented farming, like Africa and Asia, computer vision can allow farmers to manage more land or pursue other work, potentially adding billions in value.
By leveraging computer vision development services, farmers can unlock new opportunities and solve critical challenges in agriculture.
Exploring computer vision use cases and adopting advanced technologies can position agricultural businesses for sustained growth and innovation.
Future Predictions for Computer Vision in Agriculture
Technological advancements and a push towards the sustainability of farming are making computer vision in agriculture increasingly promising in the future.
Gartner provides insights around several fundamental predictions and trends in computer vision that we expect to impact the adoption and deployment of computer vision technologies in the agriculture industry.
1. The Trend in the Adoption of AI and Automation
Computer vision, used in conjunction with artificial intelligence and machine learning, is meant to help make agriculture more efficient.
When farmers are short on labour and pay climbs, AI-driven computer vision solutions can monitor crops, estimate yields, and detect pests for them.
This kind of automation is a sign of increased productivity and significant cost savings, which can make farms run more efficiently.
2. Improved Agricultural Practices with Increased Precision
With the increasing use of computer vision technologies, precision agriculture is likely to transform and become more targeted.
For example, accurately assessing the field conditions can assist in the rational use of water, fertilisers, and pesticides. This results in minimised waste, is economical with resources, and is generally more sustainable within agricultural operations.
On the other hand, the precise agriculture solutions market is forecasted to grow further with the demand for improved yield results and resource management.
3. Growth in Market Value
The projections also indicate that the computer vision market in the agriculture industry is set to grow very well, reaching an estimated value of USD 4.3 billion by 2025.
This shows the growing understanding of how computer vision technologies provide value and how we are enabling these next with unique sensor solutions, machine learning applications, and connectivity.
Challenges and Considerations
Gartner says that while computer vision in agriculture has an optimistic outlook, some challenges could stifle widespread adoption.
These include the up-front cost of deploying advanced technology, the requirement to train and train the hands of agro workers, and the issue of data privacy and security. Given these challenges, it will be essential that the extensive potential of computer vision technologies in the agricultural field is fully realised.
Forbes gives us insight into the downsides of implementing these computer vision systems in agriculture. Let’s investigate them a bit deeper and then find out how Computools can handle them with its software development expertise.
1. Data Quality and Integration
The primary challenge identified is obtaining high-quality data for computer vision systems. Further, these systems depend on accurate and reliable data collected from drones, sensors, cameras, etc.
Noisy or inconsistent data can mean inaccurate assessments and ineffective interventions. Besides, integrating data from different sources is technical; rigorous algorithms and good data management strategies are needed to ensure delivery.
2. High Implementation Costs
Deploying computer vision technology comes at a cost that can be quite high. Hardware, software and the technological infrastructure required may be expensive for farmers and agricultural businesses.
Smaller farms, in particular, may find finances and budgets to be a factor that can keep them from adopting advanced technologies.
In particular, this challenge necessitates that we carefully consider the return on investment and potential long-term benefits when we decide to integrate computer vision into farming operations.
3. Lack of Technical Expertise
Often, there is a paucity of skilled personnel who can effectively manage and operate computer vision systems. These advanced technologies may be beyond the ability of many farmers and agribusinesses to implement, maintain and troubleshoot.
This concludes with a gap in expertise, which can result in suboptimal utilisation of the technology and calls for training programs to equip users with essential skills required for the use of the technology successfully deployed.
4. Environmental Variability
Agricultural environments are inherently variable, impacted by weather, soil types, and crop varieties. Due to this variability, computer vision systems based on these algorithms may perform poorly and need to be customised to deal with the conditions frequently observed in the field.
However, developers have to develop such computer vision technologies so that the results are accurate across diverse farming environments.
5. Regulatory Concerns
In fact, the applications of computer vision technology in agriculture may encounter regulatory barriers. These technologies are susceptible to problems relating to data privacy, drone usage regulations, and meeting industry standards, which can complicate their deployment.
This means that stakeholders have to learn to navigate a complex world of regulations that can differ by region and may slow down the adoption of innovative solutions in the sector.
6. Resistance to Change
Over decades, farming practices have not been terribly changeable. Stakeholders’ resistance to the introduction of new technologies, such as computer vision, influences whether or not new technologies can be adopted.
One of the most important things that we really need to do is create a culture that is receptive to change and innovation in agricultural communities for the use of advanced technologies such as computer vision.
How to Handle the Challenges With Development Solutions
Integrating computer vision systems into agriculture is transformative but comes with several challenges. Software development vendors can leverage their software development expertise to provide solutions that address these hurdles effectively.
Here’s how they help agricultural businesses overcome the obstacles:
1. A vendor ensures high-quality data by implementing advanced data cleaning algorithms and robust management strategies.
Its team develops custom computer vision business solutions that integrate data from drones, sensors, and cameras. Real-time data processing enables timely interventions.
2. To mitigate financial barriers, a software development company can offer scalable and cost-effective solutions. They design modular systems that allow gradual implementation, reducing upfront expenses.
Additionally, a tailored approach can focus on optimising the return on investment by maximising long-term benefits and efficiency for farms of all sizes, including smallholders.
3. Recognising the skills gap, a computer vision development services vendor should provide intuitive user interfaces and comprehensive training programs for farmers and agribusinesses.
The solutions should be designed to operate easily, minimising the need for technical expertise. The team should also offer ongoing support to ensure smooth adoption and effective use of the technology.
4. Developers create customised computer vision development solutions to tackle variability in weather, soil, and crops. These systems are tailored to specific farming conditions, ensuring accuracy and consistency across diverse environments.
Integrating adaptive algorithms they help businesses achieve reliable results, regardless of environmental fluctuations.
5. Navigating complex regulations is crucial to deploying computer vision in agriculture. A good vendor must ensure compliance with regional data privacy laws, drone usage regulations, and industry standards.
The team must also assist businesses in creating transparent policies and documentation to streamline the approval process and facilitate adoption.
6. Fostering a culture of innovation is essential for successful adoption. Expert vendors help by engaging stakeholders with clear demonstrations of computer vision’s benefits for farming operations.
Through pilot programs and collaborative workshops, they show how solutions can drive business growth while maintaining traditional farming values.
Implementing Computer Vision Solutions in Agriculture
Implementing computer vision solutions demands a strategic approach, with a strong emphasis on selecting the right development partner.
Collaborating with our software development company, which possesses proven development expertise in agriculture industry, can simplify the integration process and maximise the performance of these transformative solutions.
How do you identify the right partner?
Choose a provider with verified expertise in agricultural applications of computer vision. Evaluate case studies and our clients’ testimonials to ensure a solid track record of delivering results, for example, a system to detect sick animals on a farm.
Why choose custom solutions?
A knowledgeable partner can design tailored solutions to address specific operational challenges in agriculture, enabling greater efficiency and productivity.
Why do you need to inquire about support and training?
Adopting new technologies also requires complete support and training to ensure they are adopted without any hiccups. This equips the agricultural workforce to utilise advanced tools effectively and embrace innovation confidently.
Imagine computer vision as a technology but, beyond that, as a differentiation game changer for the agriculture industry. This technology allows developing agricultural companies to attain sustainable growth while resolving critical issues.
For assistance with computer vision solutions, rely on Computools to guide your agricultural technology journey.
Reach out to Computools for any questions related to software development services at info@computools.com.
Computools
Software Solutions
Computools is an IT consulting and software development company that delivers innovative solutions to help businesses unlock tomorrow.








“Computools was selected through an RFP process. They were shortlisted and selected from between 5 other suppliers. Computools has worked thoroughly and timely to solve all security issues and launch as agreed. Their expertise is impressive.”