Cloud migration services are now a crucial part of how businesses worldwide embrace digital transformation. While we’ve all known about clouds since we were toddlers, these digital clouds are more intricate matters than just water and air.
They’re made up of countless files and massive amounts of data shielded by layers of safeguarding. This set-up lets businesses avoid complex hardware operations and effortlessly stay connected with their audiences.
In this article, we’ll break down what exactly cloud solutions are, explore why they’re so popular, and dive into the key strategies, benefits and risks involved. We’ll also discuss how relying on expert teams can ensure a smooth and secure data migration process.
What Is Cloud Migration?
To begin, let’s explore the basics of cloud services. What exactly is a cloud, and what functions does it serve?
‘The cloud’ stands for the servers accessible via the internet, along with the software and databases running on these servers, typically situated in data centres globally. Using the cloud means businesses don’t have to manage physical servers or run software apps on their machines.
The process of cloud migration involves transferring a portion or the entirety of a company’s digital resources, including data, applications, and services, from a company’s on-premises infrastructure to a cloud computing environment.
It essentially integrates the existing on-site resources of a company with those accessible in a remote digital space. The relocated assets can only be accessed through security measures functioning like a digital fence within the virtual platform.
Cloud Migration for Business
As per the recent cloud adoption survey conducted by O’Reilly, more than 90% of organisations are utilising cloud servers. Despite the widespread popularity of the technology, transitioning to the cloud isn’t as easy as flipping a switch.
The cloud brings forth varied work methods, deployment choices, and task-automation tools, altering the dynamics of enterprise infrastructure.
To make an informed decision, it’s crucial to understand how cloud migration specifically impacts your business.
• Start-ups
For start-ups, moving to the cloud or cloud storage means smoother and more cost-effective operations. It’s akin to renting the tech you need instead of buying it all up front. This way, start-ups can easily adjust their digital resources as they grow.
Plus, the cloud keeps everything safe and makes sure the business can keep going, even if something unexpected happens. In a nutshell, it’s like giving start-ups a flexible, budget-friendly and secure digital toolbox for their journey of growing and innovating.
• Small and Medium Businesses
Cloud migration for medium businesses and their smaller colleagues offers multiple benefits, ranging from improved operational efficiency to seamless scalability. And we all recognise the importance of ample room for potential growth, particularly for SMEs, which may benefit the most from embracing such technological advancements.
Before cloud computing, when businesses experienced rapid growth and their current IT infrastructure neared its capacity, the solution often involved a substantial investment of both time and money in deployment.
Now, with cloud infrastructure, the process is much smoother. It effortlessly scales alongside the business, eliminating the need for significant funding.
In fact, according to the WebinarCare resource, SMEs experience the greatest advantages, saving 36% more on their IT expenses through the cloud approach.
• Enterprises
Cloud shifting for enterprises became a major trend after the hit of COVID-19. Given the changing circumstances, organisations of various sizes had, to different extents, committed resources to establishing remote infrastructure for facilitating work-from-home set-ups.
Moving to the cloud means leaving behind outdated technologies that slow down your enterprise’s business processes. Instead of sticking with old and expensive systems that struggle with modern tech changes, going to the cloud is a smart move for the future.
Companies not only save money and scale easily right away but also set the stage to quickly adapt to market shifts, grow smoothly and foster innovation in the long run.
Benefits and Challenges of Cloud Migration
The benefits of cloud migration are numerous for both small and large companies. If SMEs are more concerned with cost savings, then enterprises are thinking about privacy and effective data processing methods.
Cloud technologies empower businesses with the tools and flexibility needed to resolve most of these issues and stay competitive in today’s market.
Here are some key benefits of cloud migration.
1. Scalability
Cloud platforms provide the flexibility to scale resources up or down based on demand, ensuring that businesses can adapt to changing needs without incurring unnecessary costs.
2. Cost Reduction
Cloud migration often leads to cost savings by eliminating the need for extensive physical infrastructure, maintenance and associated expenses, allowing businesses to pay only for the resources they use.
3. Mobility
Employees can access data and applications from anywhere with an internet connection, fostering greater mobility and facilitating remote work, leading to improved collaboration and productivity.
4. Valuable Insights
Cloud platforms offer advanced analytics and data processing capabilities, allowing businesses to extract valuable insights from their data, leading to informed decision-making and strategic planning.
5. Agile Application Development
In cloud-based development environments, teams can swiftly initiate a DevTest set-up and commence coding within minutes, a process that could otherwise take days or weeks when developers are required to order and provision new hardware.
6. Self-Service Options
Cloud services often come with self-service options, enabling teams to provision resources and deploy applications independently, reducing reliance on IT support and streamlining operations.
Nevertheless, there are two sides to every coin, and cloud technologies are no exception, presenting a unique set of challenges. The most common cloud migration challenges and concerns include:
7. Data Security
Ensuring the security of sensitive information during migration is a paramount challenge. The risk of data breaches or unauthorised access increases during the transfer process, emphasising the need for robust encryption, access controls and comprehensive security protocols.
8. Organisational Issues
The shift to a new data environment often requires organisational adjustments. Employees may need training to adapt to new systems, and there might be resistance to change.
Effective communication and change management strategies are crucial to addressing these challenges and ensuring a smooth transition.
9. Cost Considerations
Data migration involves costs related to technology, training and potential downtime. Organisations need to carefully evaluate and plan for these expenses, considering the overall return on investment (ROI) and long-term benefits of the migration.
learn more about cloud migration for your business.
Contact us →Cloud Service Models
Cloud service models refer to the categories under which cloud services are offered, defining the level of control and responsibility users have over their infrastructure and applications.
The three primary models are software as a service (SaaS), platform as a service (PaaS), and infrastructure as a service (IaaS).
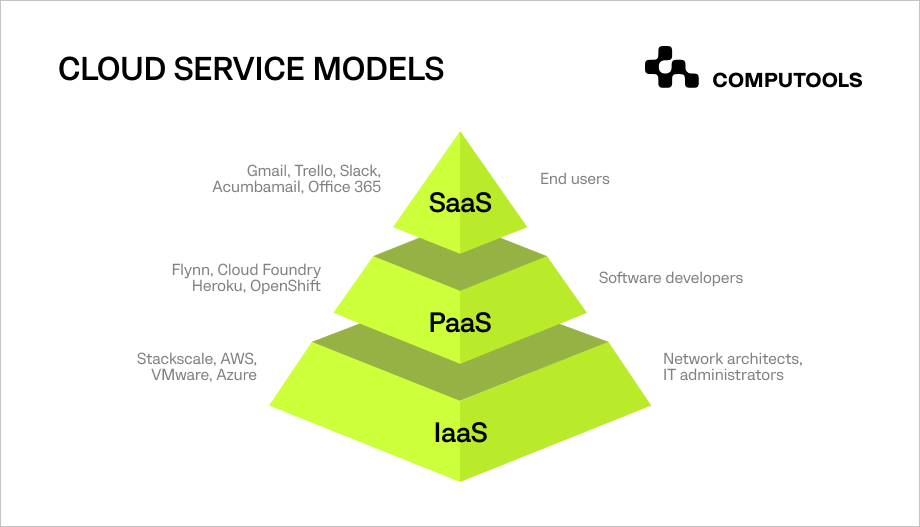
1. Software as a Service
In the software as a service (SaaS) cloud model, providers deliver fully operational software applications. Users benefit from ready-to-use applications without the burden of managing infrastructure, updates or maintenance.
SaaS applications, operating in the cloud, are typically available via desktops, mobile applications and web interfaces.
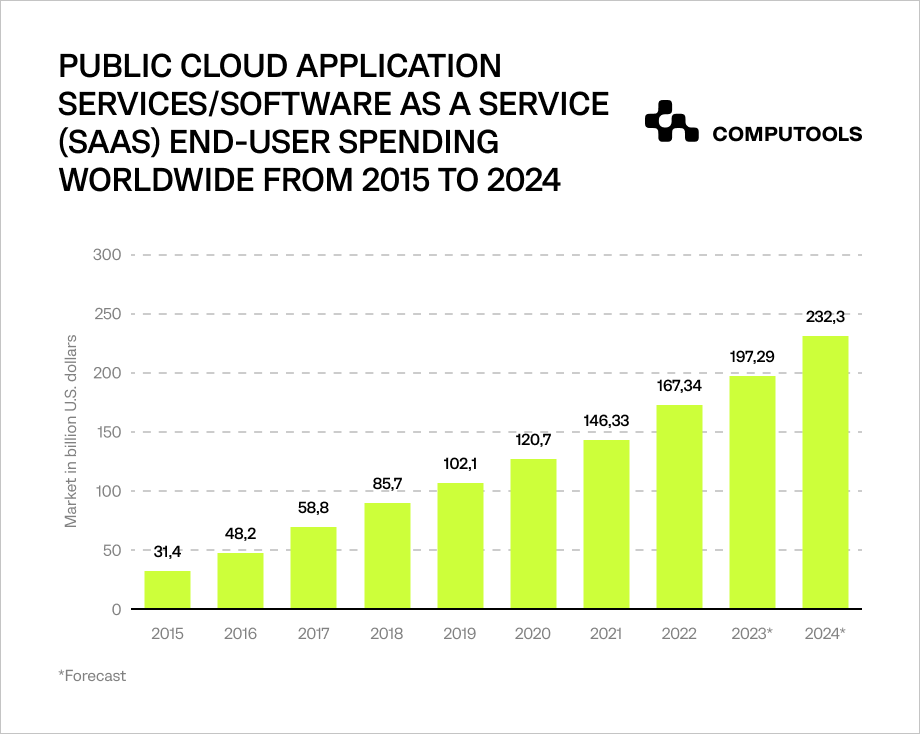
Businesses often choose SaaS for tasks such as customer relationship management, collaborative productivity or streamlined data storage. According to Statista, by the end of 2023, the value of the SaaS market is projected to be around US$197 billion.
2. Platform as a Service
The platform as a service (PaaS) is a model that offers a platform for users to develop, run and manage applications. PaaS providers furnish tools and services to streamline the development process.
Platform as a service is particularly beneficial for developers looking to deploy applications without the need to manage intricate server configurations.
3. Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS)
Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS) provides virtualised computing resources over the internet. Users have more control over operating systems, applications and development frameworks, making it a flexible choice for diverse infrastructure needs.
Examples of IaaS providers include Amazon Web Services (AWS), Microsoft Azure and Google Cloud Platform (GCP). Organisations often choose IaaS for scalable computing resources, allowing for comprehensive control over the server environment.
Cloud Migration Strategies
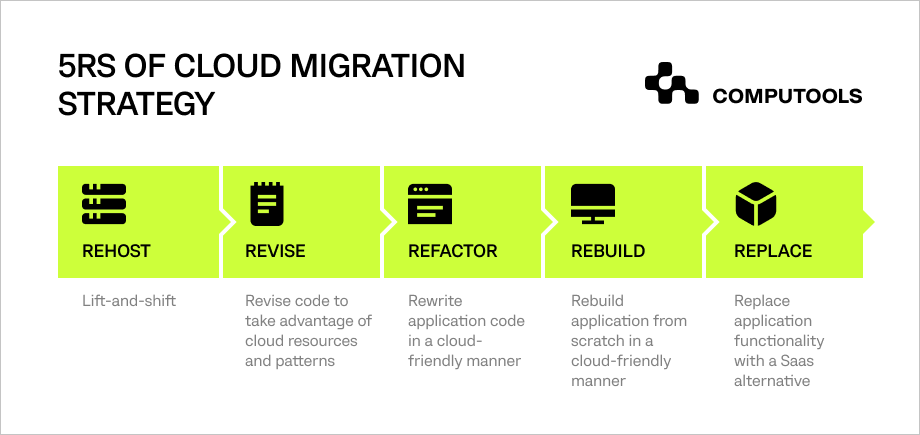
Almost 13 years ago, Gartner created the 5 Rs framework, a simple guide for moving applications to the cloud. Since then, Gartner has improved it, and giant enterprises like AWS use a similar model to plan their cloud migration strategies. Gartner’s types of cloud migration mentions the following strategies.
1. Rehost
Rehosting, also called lift-and-shift, involves moving applications to the cloud without making significant modifications. It’s a quick migration method that allows organisations to benefit from cloud infrastructure without redesigning the application.
2. Refactor
Refactoring entails making adjustments to the application’s code or architecture to optimise it for the cloud. This approach aims to improve performance, scalability and efficiency without a complete overhaul.
3. Revise/Replatform
Revising involves making modifications to the application, but not to the extent of a complete redesign. It allows for adjustments to meet specific cloud requirements without a full transformation.
4. Rebuild
Rebuilding is a more extensive transformation where the application is re-architected or reimplemented using cloud-native technologies. It often involves rewriting the codebase for better integration with cloud services.
5. Replace/Repurchase
Replacing involves discarding the existing application and adopting a new one, either through a different vendor’s solution or a completely different technology stack.
It is a strategic move for organisations seeking a fresh start with advanced features.
Developing a robust strategy for each application is vital in crafting an effective roadmap for cloud migration in a business context. The chosen strategy significantly influences the outcomes of cloud migration for business, highlighting the importance of frameworks like the 5 Rs.
How Does Cloud Migration Work?
The strategy for the cloud migration process sets the groundwork for businesses to figure out the best way to move applications to a modern infrastructure.
Even though there are different ways to migrate to the cloud, the key stages in cloud migration architecture stay the same. Here’s a simple guide on how to make cloud migration work.
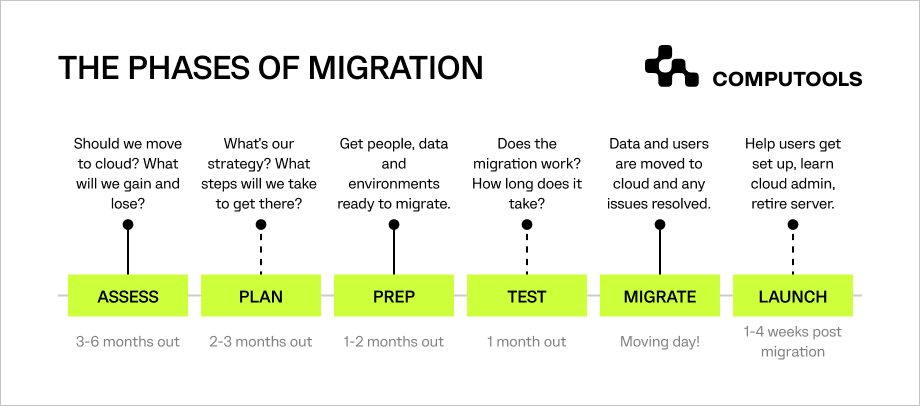
1. Assessment and Planning
Before making the move to the cloud, clearly define what you aim to achieve with the migration – set some goals and communicate them with the contractor. Use performance indicators to see how things are going.
2. Choosing a Cloud Model
During this stage, organisations decide on the type of cloud deployment that best suits their needs. This decision involves evaluating whether to opt for a public cloud, where resources are shared among multiple users, a private cloud, providing dedicated infrastructure, or a hybrid model.
3. Select Migration Strategy
Each strategy involves a different level of transformation. The decision on a migration strategy should be based on factors like urgency, optimisation goals and long-term objectives.
4. Migration
This stage involves data migration to cloud as well as application and infrastructure migration.
To perform these tasks, it’s crucial to find a team with proper expertise to ensure a seamless transition, addressing the intricacies of moving data, adapting applications and configuring the infrastructure to align with the chosen cloud environment.
5. Optimisation and Testing
When optimising and testing, the focus is on performance monitoring of migrated applications and infrastructure.
Simultaneously, developers conduct user acceptance testing (UAT) to ensure that the migrated applications align with user expectations and business requirements.
6. Post-Migration Support
Cloud migration for businesses is a dynamic process that requires careful planning, execution, and continuous improvement. Help your staff to adopt new mechanisms and algorithms.
Make sure the development team you’re working with are quick in resolving any issues that may arise after migration, refining configurations based on performance data and monitoring ongoing system performance, providing support to end-users.
Things to Consider Before Cloud Migration
1. Choosing a Partner with Subject Matter Expertise
Choosing the right cloud migration partner is crucial for a successful transition. Look for a partner with a proven track record and cloud development case studies in their portfolio that showcase their expertise.
It’s essential that the team understand the specific needs and intricacies of your business and have the technical proficiency necessary to ensure a smooth and effective migration process.
2. Compliance and Regulation
Cloud software development services do not only involve creating applications, they also encompass the responsibility of adhering to regulatory standards.
You should understand the legal implications of moving data and applications to the cloud, taking steps to mitigate any potential regulatory challenges that may arise during the migration process.
3. Scalability and Future Needs
Evaluate the scalability of the chosen cloud solutions. Assess how well it aligns with the anticipated future needs of your business. A scalable solution ensures that your cloud infrastructure can seamlessly adapt and grow as your organisation evolves.
Conclusion
In the journey of business evolution, moving to the cloud becomes a game-changer. When companies choose cloud migration for business, it’s not only about boosting efficiency and scalability, it’s about rewriting the success story.
Cloud software development is the practical tool that shapes a new narrative, transforming how businesses operate in the digital landscape.
If you have any questions about cloud migration services, please email us at info@computools.com.








Computools was selected through an RFP process. They were shortlisted and selected from between 5 other suppliers. Computools has worked thoroughly and timely to solve all security issues and launch as agreed. Their expertise is impressive.